The Cardiomyocyte RNA-Binding Proteome: Links to Intermediary Metabolism and Heart Disease
- PMID: 27452465
- PMCID: PMC4977271
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.06.084
The Cardiomyocyte RNA-Binding Proteome: Links to Intermediary Metabolism and Heart Disease
Abstract
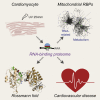
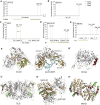
RNA functions through the dynamic formation of complexes with RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) in all clades of life. We determined the RBP repertoire of beating cardiomyocytic HL-1 cells by jointly employing two in vivo proteomic methods, mRNA interactome capture and RBDmap. Together, these yielded 1,148 RBPs, 391 of which are shared with all other available mammalian RBP repertoires, while 393 are thus far unique to cardiomyocytes. RBDmap further identified 568 regions of RNA contact within 368 RBPs. The cardiomyocyte mRNA interactome composition reflects their unique biology. Proteins with roles in cardiovascular physiology or disease, mitochondrial function, and intermediary metabolism are all highly represented. Notably, we identified 73 metabolic enzymes as RBPs. RNA-enzyme contacts frequently involve Rossmann fold domains with examples in evidence of both, mutual exclusivity of, or compatibility between RNA binding and enzymatic function. Our findings raise the prospect of previously hidden RNA-mediated regulatory interactions among cardiomyocyte gene expression, physiology, and metabolism.
Copyright © 2016 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures





References
-
- Antonicka H., Shoubridge E.A. Mitochondrial RNA granules are centers for posttranscriptional RNA processing and ribosome biogenesis. Cell Rep. 2015;10:920–932. - PubMed
-
- Balsa E., Marco R., Perales-Clemente E., Szklarczyk R., Calvo E., Landázuri M.O., Enríquez J.A. NDUFA4 is a subunit of complex IV of the mammalian electron transport chain. Cell Metab. 2012;16:378–386. - PubMed
-
- Baltz A.G., Munschauer M., Schwanhäusser B., Vasile A., Murakawa Y., Schueler M., Youngs N., Penfold-Brown D., Drew K., Milek M. The mRNA-bound proteome and its global occupancy profile on protein-coding transcripts. Mol. Cell. 2012;46:674–690. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

