Clinical Outcomes for Patients with Gleason Score 9-10 Prostate Adenocarcinoma Treated With Radiotherapy or Radical Prostatectomy: A Multi-institutional Comparative Analysis
- PMID: 27452951
- PMCID: PMC10262972
- DOI: 10.1016/j.eururo.2016.06.046
Clinical Outcomes for Patients with Gleason Score 9-10 Prostate Adenocarcinoma Treated With Radiotherapy or Radical Prostatectomy: A Multi-institutional Comparative Analysis
Abstract
Background: The long natural history of prostate cancer (CaP) limits comparisons of efficacy between radical prostatectomy (RP) and external beam radiotherapy (EBRT), since patients treated years ago received treatments considered suboptimal by modern standards (particularly with regards to androgen deprivation therapy [ADT] and radiotherapy dose-escalation]. Gleason score (GS) 9-10 CaP is particularly aggressive, and clinically-relevant endpoints occur early, facilitating meaningful comparisons.
Objective: To compare outcomes of patients with GS 9-10 CaP following EBRT, extremely-dose escalated radiotherapy (as exemplified by EBRT+brachytherapy [EBRT+BT]), and RP.
Design, setting, participants: Retrospective analysis of 487 patients with biopsy GS 9-10 CaP treated between 2000 and 2013 (230 with EBRT, 87 with EBRT+BT, and 170 with RP). Most radiotherapy patients received ADT and dose-escalated radiotherapy.
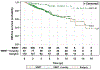
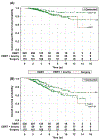
Outcome measurements and statistical analysis: Kaplan-Meier analysis and multivariate Cox regression estimated and compared 5-yr and 10-yr rates of distant metastasis-free survival, cancer-specific survival (CSS), and overall survival (OS).
Results and limitations: The median follow-up was 4.6 yr. Local salvage and systemic salvage were performed more frequently in RP patients (49.0% and 30.1%) when compared with either EBRT patients (0.9% and 19.7%) or EBRT+BT patients (1.2% and 16.1%, p<0.0001). Five-yr and 10-yr distant metastasis-free survival rates were significantly higher with EBRT+BT (94.6% and 89.8%) than with EBRT (78.7% and 66.7%, p=0.0005) or RP (79.1% and 61.5%, p<0.0001). The 5-yr and 10-yr CSS and OS rates were similar across all three cohorts.
Conclusions: Radiotherapy and RP provide equivalent CSS and OS. Extremely dose-escalated radiotherapy with ADT in particular offers improved systemic control when compared with either EBRT or RP. These data suggest that extremely dose-escalated radiotherapy with ADT might be the optimal upfront treatment for patients with biopsy GS 9-10 CaP.
Patient summary: While some prostate cancers are slow-growing requiring many years, sometimes decades, of follow-up in order to compare between radiation and surgery, high-risk and very aggressive cancers follow a much shorter time course allowing such comparisons to be made and updated as treatments, especially radiation, rapidly evolve. We showed that radiation-based treatments and surgery, with contemporary standards, offer equivalent survival for patients with very aggressive cancers (defined as Gleason score 9-10). Extremely-dose escalated radiotherapy with short-course androgen deprivation therapy offered the least risk of developing metastases, and equivalent long term survival.
Keywords: Gleason 10; Gleason 9; Radical prostatectomy; Radiotherapy.
Copyright © 2016 European Association of Urology. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
Local Therapy for Gleason 9-10 Prostate Cancer: Looking to the Future.Eur Urol. 2017 May;71(5):774-775. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2016.07.025. Epub 2016 Jul 29. Eur Urol. 2017. PMID: 27481178 No abstract available.
-
Re: Clinical Outcomes for Patients with Gleason Score 9-10 Prostate Adenocarcinoma Treated With Radiotherapy or Radical Prostatectomy: A Multi-institutional Comparative Analysis.Eur Urol. 2016 Dec;70(6):1079-1080. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2016.08.030. Epub 2016 Aug 25. Eur Urol. 2016. PMID: 27567208 No abstract available.
-
Re: Amar U. Kishan, Talha Shaikh, Pin-Chieh Wang, et al. Clinical Outcomes for Patients with Gleason Score 9-10 Prostate Adenocarcinoma Treated With Radiotherapy or Radical Prostatectomy: A Multi-institutional Comparative Analysis. Eur Urol 2017;71:766-73.Eur Urol. 2017 Nov;72(5):e121-e122. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2017.01.018. Epub 2017 Jan 17. Eur Urol. 2017. PMID: 28108149 No abstract available.
-
Reply to Thomas Van den Broeck, R. Jeffrey Karnes, and Steven Joniau's Letter to the Editor re: Amar U. Kishan, Talha Shaikh, Pin-Chieh Wang, et al. Clinical Outcomes for Patients with Gleason Score 9-10 Prostate Adenocarcinoma Treated With Radiotherapy or Radical Prostatectomy: A Multi-institutional Comparative Analysis. Eur Urol 2017;71:766-73.Eur Urol. 2017 Nov;72(5):e123-e124. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2017.01.017. Epub 2017 Jan 19. Eur Urol. 2017. PMID: 28111115 No abstract available.
-
[Combination of percutaneous radiotherapy, brachytherapy, and androgen deprivation equivalent alternatives to radical prostatectomy for prostate cancer].Strahlenther Onkol. 2018 Apr;194(4):360-362. doi: 10.1007/s00066-018-1273-7. Strahlenther Onkol. 2018. PMID: 29404627 German. No abstract available.
References
-
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin 2013;63:11–30. - PubMed
-
- Network NCC. NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology: Prostate Cancer 2015. (updated 11/10/201511/30/2015). Version I. http://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/prostate.pdf.
-
- Mottet N, Bellmunt J, Briers E, et al. EUA-ESTRO-SIOG Guidelines for Prostate Cancer 2016. [cited 2016 May 21]. http://uroweb.org/wp-content/uploads/EAU-Guidelines-Prostate-Cancer-2016....
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

