Photoswitchable diacylglycerols enable optical control of protein kinase C
- PMID: 27454932
- PMCID: PMC6101201
- DOI: 10.1038/nchembio.2141
Photoswitchable diacylglycerols enable optical control of protein kinase C
Abstract
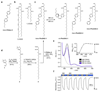
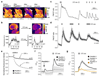
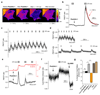
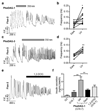
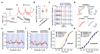
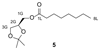
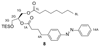
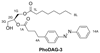
Increased levels of the second messenger lipid diacylglycerol (DAG) induce downstream signaling events including the translocation of C1-domain-containing proteins toward the plasma membrane. Here, we introduce three light-sensitive DAGs, termed PhoDAGs, which feature a photoswitchable acyl chain. The PhoDAGs are inactive in the dark and promote the translocation of proteins that feature C1 domains toward the plasma membrane upon a flash of UV-A light. This effect is quickly reversed after the termination of photostimulation or by irradiation with blue light, permitting the generation of oscillation patterns. Both protein kinase C and Munc13 can thus be put under optical control. PhoDAGs control vesicle release in excitable cells, such as mouse pancreatic islets and hippocampal neurons, and modulate synaptic transmission in Caenorhabditis elegans. As such, the PhoDAGs afford an unprecedented degree of spatiotemporal control and are broadly applicable tools to study DAG signaling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures



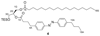

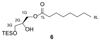


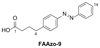
References
-
- Almena M, Mérida I. Shaping up the membrane: diacylglycerol coordinates spatial orientation of signaling. Trends Biochem Sci. 2011;36:593–603. - PubMed
-
- Brose N, Rosenmund C. Move over protein kinase C, you’ve got company: alternative cellular effectors of diacylglycerol and phorbol esters. J Cell Sci. 2002;115:4399–4411. - PubMed
-
- Newton AC. Protein Kinase C : Structure, Function, and Regulation. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:28495–28498. - PubMed
-
- Pessin MS, Raben DM. Molecular species analysis of 1,2-diglycerides stimulated by alpha-thrombin in cultured fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1989;264:8729–8738. - PubMed
-
- Marignani PA, Epand RM, Sebaldt RJ. Acyl Chain Dependence of Diacylglycerol Activation of Protein Kinase C Activity in Vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1996;473:469–473. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- PubChem-Substance/315492946
- PubChem-Substance/315492947
- PubChem-Substance/315492948
- PubChem-Substance/315492949
- PubChem-Substance/315492950
- PubChem-Substance/315492951
- PubChem-Substance/315492952
- PubChem-Substance/315492953
- PubChem-Substance/315492954
- PubChem-Substance/315492955
- PubChem-Substance/315492956
- PubChem-Substance/315492957
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

