The Effects of Aquaporin-1 in Pulmonary Edema Induced by Fat Embolism Syndrome
- PMID: 27455237
- PMCID: PMC4964552
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms17071183
The Effects of Aquaporin-1 in Pulmonary Edema Induced by Fat Embolism Syndrome
Abstract
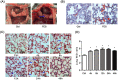
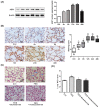
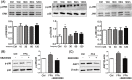
This study was designed to investigate the role of aquaporin1 (AQP1) in the pathologic process of pulmonary edema induced by fat embolism syndrome (FES) and the effects of a free fatty acid (FFA) mixture on AQP1 expression in pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells (PMVECs). In vivo, edema was more serious in FES mice compared with the control group. The expression of AQP1 and the wet-to-dry lung weight ratio (W/D) in the FES group were significantly increased compared with the control group. At the same time, inhibition of AQP1 decreased the pathological damage resulting from pulmonary edema. Then we performed a study in vitro to investigate whether AQP1 was induced by FFA release in FES. The mRNA and protein level of AQP1 were increased by FFAs in a dose- and time-dependent manner in PMVECs. In addition, the up-regulation of AQP1 was blocked by the inhibitor of p38 kinase, implicating the p38 MAPK pathway as involved in the FFA-induced AQP1 up-regulation in PMVECs. Our results demonstrate that AQP1 may play important roles in pulmonary edema induced by FES and can be regarded as a new therapy target for treatment of pulmonary edema induced by FES.
Keywords: AQP1; fat embolism syndrome; free fatty acid; p38 MAPK signaling pathway; pulmonary edema.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Specific inhibition of AQP1 water channels in human pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells by small interfering RNAs.J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2012 Jan;72(1):150-61. doi: 10.1097/TA.0b013e318230e25d. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2012. PMID: 22310126
-
AQP1 expression alterations affect morphology and water transport in Schwann cells and hypoxia-induced up-regulation of AQP1 occurs in a HIF-1α-dependent manner.Neuroscience. 2013 Nov 12;252:68-79. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.08.006. Epub 2013 Aug 12. Neuroscience. 2013. PMID: 23948641
-
The role of aquaporin-1 (AQP1) expression in a murine model of lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury.Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2004 Aug 20;142(1):1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.resp.2004.05.001. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2004. PMID: 15351300
-
[Effects of hydrogen-rich water on the expression of aquaporin 1 in the cerebral cortex of rat with traumatic brain injury].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2016 May;28(5):460-4. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2016. PMID: 29923387 Chinese.
-
From neurogenic pulmonary edema to fat embolism syndrome: a brief review of experimental and clinical investigations of acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome.Chin J Physiol. 2009 Nov 30;52(5 Suppl):339-44. doi: 10.4077/cjp.2009.amh036. Chin J Physiol. 2009. PMID: 20359124 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of Internal Exposure of Radioactive 56MnO2 Particles on the Lung in C57BL Mice.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023 Apr 6;45(4):3208-3218. doi: 10.3390/cimb45040209. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37185733 Free PMC article.
-
Advanced Diagnostic Tools in Hypothermia-Related Fatalities-A Pathological Perspective.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Mar 30;14(7):739. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14070739. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38611652 Free PMC article.
-
Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung Injury Is Associated with Increased Ran-Binding Protein in Microtubule-Organizing Center (RanBPM) Molecule Expression and Mitochondria-Mediated Apoptosis Signaling Pathway in a Mouse Model.Med Sci Monit. 2020 Jul 18;26:e923172. doi: 10.12659/MSM.923172. Med Sci Monit. 2020. PMID: 32680981 Free PMC article.
-
Berberine and cinnamaldehyde together prevent lung carcinogenesis.Oncotarget. 2017 Aug 7;8(44):76385-76397. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.20059. eCollection 2017 Sep 29. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29100319 Free PMC article.
-
Aquaporins in lung health and disease: Emerging roles, regulation, and clinical implications.Respir Med. 2020 Nov-Dec;174:106193. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2020.106193. Epub 2020 Oct 17. Respir Med. 2020. PMID: 33096317 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Verkman A.S., Matthay M.A., Song Y. Aquaporin water channels and lung physiology. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2000;278:L867–L879. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

