Mutant LRP6 Impairs Endothelial Cell Functions Associated with Familial Normolipidemic Coronary Artery Disease
- PMID: 27455246
- PMCID: PMC4964544
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms17071173
Mutant LRP6 Impairs Endothelial Cell Functions Associated with Familial Normolipidemic Coronary Artery Disease
Abstract
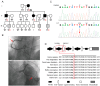
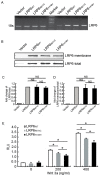
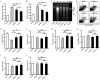
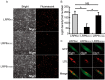
Mutations in the genes low-density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor-related protein-6 (LRP6) and myocyte enhancer factor 2A (MEF2A) were reported in families with coronary artery disease (CAD). We intend to determine the mutational spectrum of these genes among hyperlipidemic and normolipidemic CAD families. Forty probands with early-onset CAD were recruited from 19 hyperlipidemic and 21 normolipidemic Chinese families. We sequenced all exons and intron-exon boundaries of LRP6 and MEF2A, and found a novel heterozygous variant in LRP6 from a proband with normolipidemic CAD. This variant led to a substitution of histidine to tyrosine (Y418H) in an evolutionarily conserved domain YWTD in exon 6 and was not found in 1025 unrelated healthy individuals. Co-segregated with CAD in the affected family, LRP6Y418H significantly debilitated the Wnt3a-associated signaling pathway, suppressed endothelial cell proliferation and migration, and decreased anti-apoptotic ability. However, it exhibited no influences on low-density lipoprotein cholesterol uptake. Thus, mutation Y418H in LRP6 likely contributes to normolipidemic familial CAD via impairing endothelial cell functions and weakening the Wnt3a signaling pathway.
Keywords: LDL receptor-related protein-6 (LRP6); coronary artery disease; endothelial cell dysfunction; familial; normolipidemic.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Functional analysis LRP6 novel mutations in patients with coronary artery disease.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 10;9(1):e84345. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084345. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24427284 Free PMC article.
-
Rare nonconservative LRP6 mutations are associated with metabolic syndrome.Hum Mutat. 2013 Sep;34(9):1221-5. doi: 10.1002/humu.22360. Epub 2013 Jun 18. Hum Mutat. 2013. PMID: 23703864 Free PMC article.
-
Association of common polymorphisms in the LRP6 gene with sporadic coronary artery disease in a Chinese population.Chin Med J (Engl). 2012 Feb;125(3):444-9. Chin Med J (Engl). 2012. PMID: 22490400
-
Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor-Related Protein 6 (LRP6) Is a Novel Nutritional Therapeutic Target for Hyperlipidemia, Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, and Atherosclerosis.Nutrients. 2015 Jun 3;7(6):4453-64. doi: 10.3390/nu7064453. Nutrients. 2015. PMID: 26046396 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Targeting of LRP6 in Cardiovascular Diseases: Challenging But Not Wnt-Possible!Can J Cardiol. 2019 Nov;35(11):1567-1575. doi: 10.1016/j.cjca.2019.06.030. Epub 2019 Jul 11. Can J Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 31679626 Review.
Cited by
-
LRP6 Polymorphisms Is Associated With Sudden Cardiac Death in Patients With Chronic Heart Failure in the Chinese Han Population.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Feb 4;8:815595. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.815595. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 35187114 Free PMC article.
-
Foam Cells in Atherosclerosis: Novel Insights Into Its Origins, Consequences, and Molecular Mechanisms.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Apr 13;9:845942. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.845942. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 35498045 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of long non-coding RNAs in cardiovascular diseases: A comprehensive review.Noncoding RNA Res. 2024 Dec 28;11:158-187. doi: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2024.12.009. eCollection 2025 Apr. Noncoding RNA Res. 2024. PMID: 39896344 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Role for Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor-Related Protein 6 in Blood Vessel Regression in Wound Healing.Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2020 Jan 1;9(1):1-8. doi: 10.1089/wound.2019.1019. Epub 2019 Dec 6. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2020. PMID: 31871825 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiomyocyte-Restricted Low Density Lipoprotein Receptor-Related Protein 6 (LRP6) Deletion Leads to Lethal Dilated Cardiomyopathy Partly Through Drp1 Signaling.Theranostics. 2018 Jan 1;8(3):627-643. doi: 10.7150/thno.22177. eCollection 2018. Theranostics. 2018. PMID: 29344294 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Go A.S., Mozaffarian D., Roger V.L., Benjamin E.J., Berry J.D., Blaha M.J., Dai S., Ford E.S., Fox C.S., Franco S., et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2014 update: A report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2014;129 doi: 10.1161/01.cir.0000442015.53336.12. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

