Ectromelia Virus Disease Characterization in the BALB/c Mouse: A Surrogate Model for Assessment of Smallpox Medical Countermeasures
- PMID: 27455306
- PMCID: PMC4974538
- DOI: 10.3390/v8070203
Ectromelia Virus Disease Characterization in the BALB/c Mouse: A Surrogate Model for Assessment of Smallpox Medical Countermeasures
Abstract
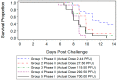
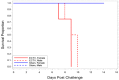
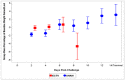
In 2007, the United States- Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued guidance concerning animal models for testing the efficacy of medical countermeasures against variola virus (VARV), the etiologic agent for smallpox. Ectromelia virus (ECTV) is naturally-occurring and responsible for severe mortality and morbidity as a result of mousepox disease in the murine model, displaying similarities to variola infection in humans. Due to the increased need of acceptable surrogate animal models for poxvirus disease, we have characterized ECTV infection in the BALB/c mouse. Mice were inoculated intranasally with a high lethal dose (125 PFU) of ECTV, resulting in complete mortality 10 days after infection. Decreases in weight and temperature from baseline were observed eight to nine days following infection. Viral titers via quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) and plaque assay were first observed in the blood at 4.5 days post-infection and in tissue (spleen and liver) at 3.5 days post-infection. Adverse clinical signs of disease were first observed four and five days post-infection, with severe signs occurring on day 7. Pathological changes consistent with ECTV infection were first observed five days after infection. Examination of data obtained from these parameters suggests the ECTV BALB/c model is suitable for potential use in medical countermeasures (MCMs) development and efficacy testing.
Keywords: BALB/c; antiviral; ectromelia; medical countermeasure; smallpox; surrogate model; vaccine.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Identification of a novel ectromelia virus from rodent: Implications for use as an in vivo infection model for vaccine and antiviral research.Virol Sin. 2025 Aug;40(4):601-612. doi: 10.1016/j.virs.2025.07.001. Epub 2025 Jul 7. Virol Sin. 2025. PMID: 40633843
-
The genome sequence of ectromelia virus Naval and Cornell isolates from outbreaks in North America.Virology. 2014 Aug;462-463:218-26. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2014.06.010. Epub 2014 Jul 5. Virology. 2014. PMID: 24999046 Free PMC article.
-
Propagation and Purification of Ectromelia Virus.Curr Protoc Microbiol. 2018 Nov;51(1):e65. doi: 10.1002/cpmc.65. Epub 2018 Oct 3. Curr Protoc Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30281950
-
Ectromelia virus: the causative agent of mousepox.J Gen Virol. 2005 Oct;86(Pt 10):2645-2659. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.81090-0. J Gen Virol. 2005. PMID: 16186218 Review.
-
The Pathogenesis and Immunobiology of Mousepox.Adv Immunol. 2016;129:251-76. doi: 10.1016/bs.ai.2015.10.001. Epub 2015 Nov 21. Adv Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26791861 Review.
Cited by
-
Orthopoxvirus Zoonoses-Do We Still Remember and Are Ready to Fight?Pathogens. 2023 Feb 21;12(3):363. doi: 10.3390/pathogens12030363. Pathogens. 2023. PMID: 36986285 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rabbitpox in New Zealand White Rabbits: A Therapeutic Model for Evaluation of Poxvirus Medical Countermeasures Under the FDA Animal Rule.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018 Oct 5;8:356. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2018.00356. eCollection 2018. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30345258 Free PMC article.
-
DNA-Sensing Antiviral Innate Immunity in Poxvirus Infection.Front Immunol. 2020 Aug 28;11:1637. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01637. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32983084 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ophthalmic Features and Implications of Poxviruses: Lessons from Clinical and Basic Research.Microorganisms. 2022 Dec 15;10(12):2487. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10122487. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 36557740 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synergistic effect of two human-like monoclonal antibodies confers protection against orthopoxvirus infection.Nat Commun. 2024 Apr 16;15(1):3265. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-47328-y. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38627363 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fenner F., Henderson D.A., Arita I., Jezek Z., Ladnyi I.D. History of International and Public Health. Volume 6 World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 1988. Smallpox and its Eradication.
-
- Marchal J. Infectious ectromelia: A hitherto undescribed virus disease in mice. J. Pathol. Bacteriol. 1930;33:713–728. doi: 10.1002/path.1700330317. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

