Genome-wide association analyses identify new risk variants and the genetic architecture of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- PMID: 27455348
- PMCID: PMC5556360
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.3622
Genome-wide association analyses identify new risk variants and the genetic architecture of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
Abstract
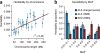
To elucidate the genetic architecture of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and find associated loci, we assembled a custom imputation reference panel from whole-genome-sequenced patients with ALS and matched controls (n = 1,861). Through imputation and mixed-model association analysis in 12,577 cases and 23,475 controls, combined with 2,579 cases and 2,767 controls in an independent replication cohort, we fine-mapped a new risk locus on chromosome 21 and identified C21orf2 as a gene associated with ALS risk. In addition, we identified MOBP and SCFD1 as new associated risk loci. We established evidence of ALS being a complex genetic trait with a polygenic architecture. Furthermore, we estimated the SNP-based heritability at 8.5%, with a distinct and important role for low-frequency variants (frequency 1-10%). This study motivates the interrogation of larger samples with full genome coverage to identify rare causal variants that underpin ALS risk.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


References
-
- Hardiman O, van den Berg LH, Kiernan MC. Clinical diagnosis and management of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nat Rev Neurol. 2011;7:639–649. - PubMed
-
- van Es MA, et al. Genome-wide association study identifies 19p13.3 (UNC13A) and 9p21.2 as susceptibility loci for sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nat Genet. 2009;41:1083–1087. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- JONES/OCT15/958-799/MNDA_/Motor Neurone Disease Association/United Kingdom
- MC_G1000733/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0600974/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/M008606/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MALASPINA/APR13/817-791/MNDA_/Motor Neurone Disease Association/United Kingdom
- FRATTA/JAN15/946-795/MNDA_/Motor Neurone Disease Association/United Kingdom
- SMITH/APR16/847-791/MNDA_/Motor Neurone Disease Association/United Kingdom
- G0900688/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G-1107/PUK_/Parkinson's UK/United Kingdom
- MRF-060-0003-RG-SMITH/MRF_/MRF_/United Kingdom
- G0901254/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- P01 AG032953/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- MR/K000039/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MR/L501529/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- P01 AG017586/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- MC_G0901330/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 NS073873/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- MCLAUGHLIN/OCT15/957-799/MNDA_/Motor Neurone Disease Association/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

