Injectable and Glucose-Responsive Hydrogels Based on Boronic Acid-Glucose Complexation
- PMID: 27455412
- PMCID: PMC5242094
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.5b04755
Injectable and Glucose-Responsive Hydrogels Based on Boronic Acid-Glucose Complexation
Abstract
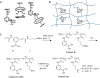
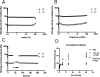
Injectable hydrogels have been widely used for a number of biomedical applications. Here, we report a new strategy to form an injectable and glucose-responsive hydrogel using the boronic acid-glucose complexation. The ratio of boronic acid and glucose functional groups is critical for hydrogel formation. In our system, polymers with 10-60% boronic acid, with the balance being glucose-modified, are favorable to form hydrogels. These hydrogels are shear-thinning and self-healing, recovering from shear-induced flow to a gel state within seconds. More importantly, these polymers displayed glucose-responsive release of an encapsulated model drug. The hydrogel reported here is an injectable and glucose-responsive hydrogel constructed from the complexation of boronic acid and glucose within a single component polymeric material.
Conflict of interest statement
Notes The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Injectable Self-Healing Glucose-Responsive Hydrogels with pH-Regulated Mechanical Properties.Adv Mater. 2016 Jan 6;28(1):86-91. doi: 10.1002/adma.201502902. Epub 2015 Nov 5. Adv Mater. 2016. PMID: 26540021 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic Bonds between Boronic Acid and Alginate: Hydrogels with Stretchable, Self-Healing, Stimuli-Responsive, Remoldable, and Adhesive Properties.Biomacromolecules. 2018 Jun 11;19(6):2053-2061. doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.8b00144. Epub 2018 Apr 11. Biomacromolecules. 2018. PMID: 29601721
-
Glucose-responsive hydrogels based on dynamic covalent chemistry and inclusion complexation.Soft Matter. 2014 Apr 21;10(15):2671-8. doi: 10.1039/c3sm53059k. Soft Matter. 2014. PMID: 24647364
-
Boronic acid-containing hydrogels: synthesis and their applications.Chem Soc Rev. 2013 Oct 21;42(20):8106-21. doi: 10.1039/c3cs60152h. Chem Soc Rev. 2013. PMID: 23860617 Review.
-
Biomolecule-Responsive Hydrogels in Medicine.Adv Healthc Mater. 2017 Dec;6(24). doi: 10.1002/adhm.201700801. Epub 2017 Oct 23. Adv Healthc Mater. 2017. PMID: 29057617 Review.
Cited by
-
Injectable dynamic covalent hydrogels of boronic acid polymers cross-linked by bioactive plant-derived polyphenols.Biomater Sci. 2018 Aug 21;6(9):2487-2495. doi: 10.1039/c8bm00453f. Biomater Sci. 2018. PMID: 30069570 Free PMC article.
-
Injectable Polyethylene Glycol Hydrogel for Islet Encapsulation: an in vitro and in vivo Characterization.Biomed Phys Eng Express. 2017;3:035022. doi: 10.1088/2057-1976/aa742b. Epub 2017 Jun 14. Biomed Phys Eng Express. 2017. PMID: 29527325 Free PMC article.
-
Characterizing rheological properties and microstructure of thioester networks during degradation.Soft Matter. 2023 Oct 4;19(38):7429-7442. doi: 10.1039/d3sm00864a. Soft Matter. 2023. PMID: 37743747 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and characterization of phenylboronic acid-containing polymer for glucose-triggered drug delivery.Sci Technol Adv Mater. 2019 Dec 9;21(1):1-10. doi: 10.1080/14686996.2019.1700394. eCollection 2020. Sci Technol Adv Mater. 2019. PMID: 32002087 Free PMC article.
-
Development of glucose-responsive 'smart' insulin systems.Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2017 Aug;24(4):267-278. doi: 10.1097/MED.0000000000000345. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2017. PMID: 28509691 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Appel EA, del Barrio J, Loh XJ, Scherman OA. Supramolecular polymeric hydrogels. Chem Soc Rev. 2012;41(18):6195–214. - PubMed
-
- Appel EA, Loh XJ, Jones ST, Dreiss CA, Scherman OA. Sustained release of proteins from high water content supra-molecular polymer hydrogels. Biomaterials. 2012;33(18):4646–52. - PubMed
-
- Kanchwala SK, Holloway L, Bucky LP. Reliable soft tissue augmentation: a clinical comparison of injectable soft-tissue fillers for facial-volume augmentation. Ann Plast Surg. 2005;55(1):30–5. - PubMed
-
- Li Y, Rodrigues J, Tomas H. Injectable and biodegradable hydrogels: gelation, biodegradation and biomedical applications. Chem Soc Rev. 2012;41(6):2193–221. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

