Development of a Monte Carlo model for treatment planning dose verification of the Leksell Gamma Knife Perfexion radiosurgery system
- PMID: 27455497
- PMCID: PMC5690038
- DOI: 10.1120/jacmp.v17i4.6196
Development of a Monte Carlo model for treatment planning dose verification of the Leksell Gamma Knife Perfexion radiosurgery system
Abstract
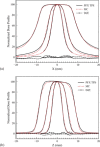
Detailed Monte Carlo (MC) modeling of the Leksell Gamma Knife (GK) Perfexion (PFX) collimator system is the only accurate ab initio approach appearing in the literature. As a different approach, in this work, we present a MC model based on film measurement. By adjusting the model parameters and fine-tuning the derived fluence map for each individual source to match the manufacturer's ring output factors, we created a reasonable virtual source model for MC simulations to verify treatment planning dose for the GK PFX radiosurgery system. The MC simulation model was commissioned by simple single shots. Dose profiles and both ring and collimator output factors were compared with the treatment planning system (TPS). Good agreement was achieved for dose profiles especially for the region of plateau (< 2%), while larger difference (< 5%) came from the penumbra region. The maximum difference of the calculated output factor was within 0.7%. The model was further validated by a clinical test case. Good agreement was obtained. The DVHs for brainstem and the skull were almost identical and, for the target, the volume covered by the prescription (12.5 Gy to 50% isodose line) was 95.6% from MC calculation versus 100% from the TPS.
© 2016 The Authors
Figures




Similar articles
-
A Monte Carlo model and its commissioning for the Leksell Gamma Knife Perfexion radiosurgery system.Med Phys. 2017 Sep;44(9):4910-4918. doi: 10.1002/mp.12402. Epub 2017 Aug 1. Med Phys. 2017. PMID: 28599073
-
MCNP-based computational model for the Leksell gamma knife.Med Phys. 2007 Jan;34(1):63-75. doi: 10.1118/1.2401054. Med Phys. 2007. PMID: 17278491
-
Application of the gamma evaluation method in Gamma Knife film dosimetry.Med Phys. 2011 Oct;38(10):5778-87. doi: 10.1118/1.3641644. Med Phys. 2011. PMID: 21992392
-
Influence of the jaw tracking technique on the dose calculation accuracy of small field VMAT plans.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2017 Jan;18(1):186-195. doi: 10.1002/acm2.12029. Epub 2017 Jan 3. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2017. PMID: 28291941 Free PMC article. Review.
-
3-D treatment planning system-Leksell Gamma Knife treatment planning system.Med Dosim. 2018 Summer;43(2):177-183. doi: 10.1016/j.meddos.2018.03.001. Epub 2018 Apr 12. Med Dosim. 2018. PMID: 29656889 Review.
Cited by
-
An Integrated Framework Based on Full Monte Carlo Simulations for Double-Scattering Proton Therapy.Int J Part Ther. 2019 Fall;6(2):31-41. doi: 10.14338/IJPT-19-00063.1. Epub 2019 Sep 5. Int J Part Ther. 2019. PMID: 31998819 Free PMC article.
-
Monte Carlo Dose Calculation Using MRI Based Synthetic CT Generated by Fully Convolutional Neural Network for Gamma Knife Radiosurgery.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2021 Jan-Dec;20:15330338211046433. doi: 10.1177/15330338211046433. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2021. PMID: 34632872 Free PMC article.
-
Stereotactic radiosurgery alone for multiple brain metastases? A review of clinical and technical issues.Neuro Oncol. 2017 Apr 1;19(suppl_2):ii2-ii15. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nox001. Neuro Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28380635 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Regis J, Tamura M, Guillot C et al. Radiosurgery with the world's first fully robotized Leksell Gamma Knife PerfeXion in clinical use: a 200‐patient prospective, randomized, controlled comparison with the Gamma Knife 4C. Neurosurgery. 2009;64(2):346–55. - PubMed
-
- Elekta Instrument AB . A new TMR dose algorithm in Leksell GammaPlan. Technical Report No. 1021357.00. Stockholm: Eleckta Instrument AB; 2011.
-
- Elekta Instrument AB . The convolution algorithm in Leksell GammaPlan 10. Technical Report No. 018881.01. Stockholm: Eleckta Instrument AB; 2010.
-
- Cheung JY, Yu KN, Ho RT, Yu CP. Monte Carlo calculated output factors of a Leksell Gamma Knife unit. Phys Med Biol. 1999;44(12):N247–N249. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

