Validation of total skin electron irradiation (TSEI) technique dosimetry data by Monte Carlo simulation
- PMID: 27455502
- PMCID: PMC5690047
- DOI: 10.1120/jacmp.v17i4.6230
Validation of total skin electron irradiation (TSEI) technique dosimetry data by Monte Carlo simulation
Abstract
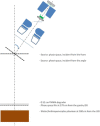
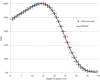
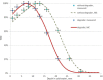
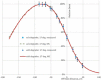
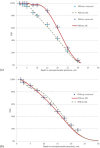
Total skin electron irradiation (TSEI) is a complex technique which requires many nonstandard measurements and dosimetric procedures. The purpose of this work was to validate measured dosimetry data by Monte Carlo (MC) simulations using EGSnrc-based codes (BEAMnrc and DOSXYZnrc). Our MC simulations consisted of two major steps. In the first step, the incident electron beam parameters (energy spectrum, FWHM, mean angular spread) were adjusted to match the measured data (PDD and profile) at SSD = 100 cm for an open field. In the second step, these parameters were used to calculate dose distributions at the treatment distance of 400 cm. MC simulations of dose distributions from single and dual fields at the treatment distance were performed in a water phantom. Dose distribution from the full treatment with six dual fields was simulated in a CT-based anthropomorphic phantom. MC calculations were compared to the available set of measurements used in clinical practice. For one direct field, MC calculated PDDs agreed within 3%/1 mm with the measurements, and lateral profiles agreed within 3% with the measured data. For the OF, the measured and calculated results were within 2% agreement. The optimal angle of 17° was confirmed for the dual field setup. Dose distribution from the full treatment with six dual fields was simulated in a CT-based anthropomorphic phantom. The MC-calculated multiplication factor (B12-factor), which relates the skin dose for the whole treatment to the dose from one calibration field, for setups with and without degrader was 2.9 and 2.8, respectively. The measured B12-factor was 2.8 for both setups. The difference between calculated and measured values was within 3.5%. It was found that a degrader provides more homogeneous dose distribution. The measured X-ray contamination for the full treatment was 0.4%; this is compared to the 0.5% X-ray contamination obtained with the MC calculation. Feasibility of MC simulation in an anthropomorphic phantom for a full TSEI treatment was proved and is reported for the first time in the literature. The results of our MC calculations were found to be in general agreement with the measurements, providing a promising tool for further studies of dose distribution calculations in TSEI.
© 2016 The Authors
Figures





Similar articles
-
Validation of the dosimetry of total skin irradiation techniques by Monte Carlo simulation.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2020 Aug;21(8):107-119. doi: 10.1002/acm2.12921. Epub 2020 Jun 19. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2020. PMID: 32559022 Free PMC article.
-
Monte Carlo techniques for scattering foil design and dosimetry in total skin electron irradiations.Med Phys. 2005 Jun;32(6):1460-8. doi: 10.1118/1.1924368. Med Phys. 2005. PMID: 16013701
-
Room scatter effects in Total Skin Electron Irradiation: Monte Carlo simulation study.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2017 Jan;18(1):196-201. doi: 10.1002/acm2.12039. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2017. PMID: 28291915 Free PMC article.
-
Dosimetry applications in GATE Monte Carlo toolkit.Phys Med. 2017 Sep;41:136-140. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmp.2017.02.005. Epub 2017 Feb 22. Phys Med. 2017. PMID: 28236558 Review.
-
USE OF ANTHROPOMORPHIC HETEROGENEOUS PHYSICAL PHANTOMS FOR VALIDATION OF COMPUTATIONAL DOSIMETRY OF MEDICAL PERSONNEL AND PATIENTS.Probl Radiac Med Radiobiol. 2020 Dec;25:148-176. doi: 10.33145/2304-8336-2020-25-148-176. Probl Radiac Med Radiobiol. 2020. PMID: 33361833 Review. English, Ukrainian.
Cited by
-
Patient Dose Analysis Using GafchromicTM EBT3 Film: A Retrospective Study with a Four Dual-Field Technique in Total Skin Electron Therapy.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2023 Jul 1;24(7):2505-2513. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2023.24.7.2505. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2023. PMID: 37505785 Free PMC article.
-
Dosimetry, Optimization and FMEA of Total Skin Electron Irradiation (TSEI).Z Med Phys. 2022 May;32(2):228-239. doi: 10.1016/j.zemedi.2021.09.004. Epub 2021 Nov 2. Z Med Phys. 2022. PMID: 34740500 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a 3D-printed phantom for total skin electron therapy dose assessment.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2024 Dec;25(12):e14520. doi: 10.1002/acm2.14520. Epub 2024 Sep 16. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2024. PMID: 39284207 Free PMC article.
-
Computational dose visualization & comparison in total skin electron treatment suggests superior coverage by the rotational versus the Stanford technique.J Med Imaging Radiat Sci. 2022 Dec;53(4):612-622. doi: 10.1016/j.jmir.2022.08.006. Epub 2022 Aug 28. J Med Imaging Radiat Sci. 2022. PMID: 36045017 Free PMC article.
-
Validation of the dosimetry of total skin irradiation techniques by Monte Carlo simulation.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2020 Aug;21(8):107-119. doi: 10.1002/acm2.12921. Epub 2020 Jun 19. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2020. PMID: 32559022 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Desai KR, Pezner RD, Lipsett JA et al. Total skin electron irradiation for mycosis fungoides: relationship between acute toxicities and measured dose at different anatomic sites. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1988;15(3):641–45. - PubMed
-
- Diamantopoulos S, Platoni K, Dilvoi M et al. Clinical implementation of total skin electron beam (TSEB) therapy: a review of the relevant literature. Phys Med. 2011;27(2):62–68. - PubMed
-
- Jones G, Wilson LD, Fox‐Goguen L. Total skin electron beam radiotherapy for patients who have mycosis fungoides. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2003;17(6):1421–34. - PubMed
-
- Anacak Y, Arican Z, Bar‐Deroma R, Tamir A, Kuten A. Total skin electron irradiation: evaluation of dose uniformity throughout the skin surface. Med Dosim. 2003;28(1):31–34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

