Full transcription of the chloroplast genome in photosynthetic eukaryotes
- PMID: 27456469
- PMCID: PMC4960489
- DOI: 10.1038/srep30135
Full transcription of the chloroplast genome in photosynthetic eukaryotes
Abstract
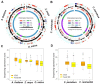
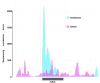
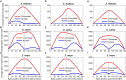
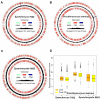
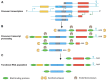
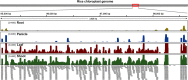
Prokaryotes possess a simple genome transcription system that is different from that of eukaryotes. In chloroplasts (plastids), it is believed that the prokaryotic gene transcription features govern genome transcription. However, the polycistronic operon transcription model cannot account for all the chloroplast genome (plastome) transcription products at whole-genome level, especially regarding various RNA isoforms. By systematically analyzing transcriptomes of plastids of algae and higher plants, and cyanobacteria, we find that the entire plastome is transcribed in photosynthetic green plants, and that this pattern originated from prokaryotic cyanobacteria - ancestor of the chloroplast genomes that diverged about 1 billion years ago. We propose a multiple arrangement transcription model that multiple transcription initiations and terminations combine haphazardly to accomplish the genome transcription followed by subsequent RNA processing events, which explains the full chloroplast genome transcription phenomenon and numerous functional and/or aberrant pre-RNAs. Our findings indicate a complex prokaryotic genome regulation when processing primary transcripts.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

