Nonmedical Prescription Opioid and Heroin Use Among Adolescents Who Engage in Sports and Exercise
- PMID: 27456508
- PMCID: PMC4960731
- DOI: 10.1542/peds.2016-0677
Nonmedical Prescription Opioid and Heroin Use Among Adolescents Who Engage in Sports and Exercise
Abstract
Objectives: Previous research has found that adolescent athletes may be at increased risk of nonmedical prescription opioid use (NPOU) due to injuries. Although adolescent athletes are at an increased risk of engaging in NPOU, it has yet to be determined if they are also at greater risk for heroin use. The major purpose of this study was to examine both the trends in prevalence rates and patterns of initiation in lifetime NPOU and lifetime heroin use among adolescents who engage in sports and exercise.
Methods: Eighteen cross-sections of eighth and 10th graders were used from the Monitoring the Future study. The sample consisted of 191 682 respondents who answered questions on past-year participation in sports and exercise, lifetime NPOU, lifetime heroin use, age of NPOU onset, and age of heroin onset.
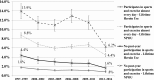
Results: The trends in NPOU and lifetime heroin use among adolescents who engage in sports and exercise has declined between 1997 and 2014. Logistic regression analyses found that adolescents who engage in sports and exercise had lower odds of reporting lifetime NPOU and heroin use compared with adolescents who did not engage in these activities during the past year. Analyses among lifetime heroin users found that adolescents who engage in sports and exercise had lower odds of initiating NPOU before heroin when compared with their peers who did not engage in these activities in the past year.
Conclusions: Daily participation in sports and exercise may serve as a protective factor with respect to NPOU and heroin use.
Copyright © 2016 by the American Academy of Pediatrics.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Fortuna RJ, Robbins BW, Caiola E, Joynt M, Halterman JS. Prescribing of controlled medications to adolescents and young adults in the United States. Pediatrics. 2010;126(6):1108–1116 - PubMed
-
- Miech RA, Johnston LD, O’Malley PM, Bachman JG, Schulenberg JE. Monitoring the Future National Survey Results on Drug Use, 1975–2014 Vol I: Secondary School Students. Ann Arbor, MI: University of Michigan Institute for Social Research; 2015
-
- Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration 2014. Results from the 2013 National Survey on Drug Use and Health: summary of national findings. In: NSDUH Series H-48, HHS Publication No. (SMA) 14-4863
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

