Mycotoxin Patulin Suppresses Innate Immune Responses by Mitochondrial Dysfunction and p62/Sequestosome-1-dependent Mitophagy
- PMID: 27458013
- PMCID: PMC5016671
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M115.686683
Mycotoxin Patulin Suppresses Innate Immune Responses by Mitochondrial Dysfunction and p62/Sequestosome-1-dependent Mitophagy
Abstract
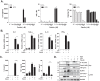
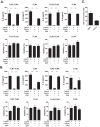
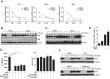
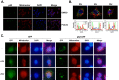
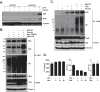
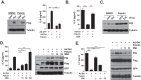
Innate immune responses are important for pathogen elimination and adaptive immune response activation. However, excess inflammation may contribute to immunopathology and disease progression (e.g. inflammation-associated hepatocellular carcinoma). Immune modulation resulting from pattern recognition receptor-induced responses is a potential strategy for controlling immunopathology and related diseases. This study demonstrates that the mycotoxin patulin suppresses Toll-like receptor- and RIG-I/MAVS-dependent cytokine production through GSH depletion, mitochondrial dysfunction, the activation of p62-associated mitophagy, and p62-TRAF6 interaction. Blockade of autophagy restored the immunosuppressive activity of patulin, and pharmacological activation of p62-dependent mitophagy directly reduced RIG-I-like receptor-dependent inflammatory cytokine production. These results demonstrated that p62-dependent mitophagy has an immunosuppressive role to innate immune response and might serve as a potential immunomodulatory target for inflammation-associated diseases.
Keywords: RIG-I-like receptor (RLR); immunomodulation; mitochondria; mitophagy; mycotoxin; p62 (sequestosome 1(SQSTM1)); patulin; toll-like receptor (TLR).
© 2016 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The ICP0 Protein of Herpes Simplex Virus 1 (HSV-1) Downregulates Major Autophagy Adaptor Proteins Sequestosome 1 and Optineurin during the Early Stages of HSV-1 Infection.J Virol. 2019 Oct 15;93(21):e01258-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01258-19. Print 2019 Nov 1. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 31375597 Free PMC article.
-
Phase separation of Nur77 mediates celastrol-induced mitophagy by promoting the liquidity of p62/SQSTM1 condensates.Nat Commun. 2021 Oct 13;12(1):5989. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-26295-8. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 34645818 Free PMC article.
-
From autophagy to mitophagy: the roles of P62 in neurodegenerative diseases.J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2017 Oct;49(5):413-422. doi: 10.1007/s10863-017-9727-7. Epub 2017 Oct 3. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2017. PMID: 28975445 Review.
-
Loss of the selective autophagy receptor p62 impairs murine myeloid leukemia progression and mitophagy.Blood. 2019 Jan 10;133(2):168-179. doi: 10.1182/blood-2018-02-833475. Epub 2018 Nov 29. Blood. 2019. PMID: 30498063
-
Mitochondria in innate immune signaling.Transl Res. 2018 Dec;202:52-68. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2018.07.014. Epub 2018 Aug 7. Transl Res. 2018. PMID: 30165038 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Is Disrupted Mitophagy a Central Player to Parkinson's Disease Pathology?Cureus. 2023 Feb 25;15(2):e35458. doi: 10.7759/cureus.35458. eCollection 2023 Feb. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 36860818 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A high-throughput gut-on-chip platform to study the epithelial responses to enterotoxins.Sci Rep. 2024 Mar 9;14(1):5797. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-56520-5. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38461178 Free PMC article.
-
Patulin Alters Insulin Signaling and Metabolic Flexibility in HepG2 and HEK293 Cells.Toxins (Basel). 2023 Mar 27;15(4):244. doi: 10.3390/toxins15040244. Toxins (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37104182 Free PMC article.
-
Glycosylation and S-palmitoylation regulate SARS-CoV-2 spike protein intracellular trafficking.iScience. 2022 Aug 19;25(8):104709. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.104709. Epub 2022 Jul 3. iScience. 2022. PMID: 35813875 Free PMC article.
-
Patulin suppresses α1-adrenergic receptor expression in HEK293 cells.Sci Rep. 2020 Nov 18;10(1):20115. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-77157-0. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33208818 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

