mito-QC illuminates mitophagy and mitochondrial architecture in vivo
- PMID: 27458135
- PMCID: PMC4970326
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201603039
mito-QC illuminates mitophagy and mitochondrial architecture in vivo
Abstract
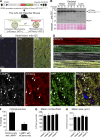
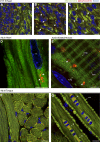
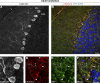
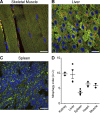
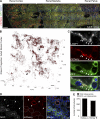
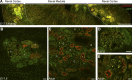
Autophagic turnover of mitochondria, termed mitophagy, is proposed to be an essential quality-control (QC) mechanism of pathophysiological relevance in mammals. However, if and how mitophagy proceeds within specific cellular subtypes in vivo remains unclear, largely because of a lack of tractable tools and models. To address this, we have developed "mito-QC," a transgenic mouse with a pH-sensitive fluorescent mitochondrial signal. This allows the assessment of mitophagy and mitochondrial architecture in vivo. Using confocal microscopy, we demonstrate that mito-QC is compatible with classical and contemporary techniques in histochemistry and allows unambiguous in vivo detection of mitophagy and mitochondrial morphology at single-cell resolution within multiple organ systems. Strikingly, our model uncovers highly enriched and differential zones of mitophagy in the developing heart and within specific cells of the adult kidney. mito-QC is an experimentally advantageous tool of broad relevance to cell biology researchers within both discovery-based and translational research communities.
© 2016 McWilliams et al.
Figures

References
-
- Bingol B., Tea J.S., Phu L., Reichelt M., Bakalarski C.E., Song Q., Foreman O., Kirkpatrick D.S., and Sheng M.. 2014. The mitochondrial deubiquitinase USP30 opposes parkin-mediated mitophagy. Nature. 510:370–375. http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature13418 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

