Failure of the Amikacin, Cefoxitin, and Clarithromycin Combination Regimen for Treating Pulmonary Mycobacterium abscessus Infection
- PMID: 27458221
- PMCID: PMC5038227
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00990-16
Failure of the Amikacin, Cefoxitin, and Clarithromycin Combination Regimen for Treating Pulmonary Mycobacterium abscessus Infection
Abstract
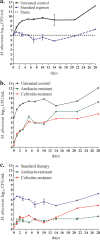
In a hollow-fiber model, we mimicked the drug exposures achieved in the lungs of humans treated with standard amikacin, clarithromycin, and cefoxitin combination therapy for Mycobacterium abscessus infection. At optimal dosing, a kill rate of -0.09 (95% confidence interval, -0.04 to 0.03) log10 CFU per ml/day was achieved over the first 14 days, after which there was regrowth due to acquired drug resistance. Thus, the standard regimen quickly failed. A new regimen is needed.
Copyright © 2016, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Griffith DE, Aksamit T, Brown-Elliott BA, Catanzaro A, Daley C, Gordin F, Holland SM, Horsburgh R, Huitt G, Iademarco MF, Iseman M, Olivier K, Ruoss S, von Reyn CF, Wallace RJ Jr, Winthrop K, ATS Mycobacterial Diseases Subcommittee, American Thoracic Society, Infectious Diseases Society of America. 2007. An official ATS/IDSA statement: diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of nontuberculous mycobacterial diseases. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 175:367–416. doi:10.1164/rccm.200604-571ST. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. 2011. Susceptibility testing of mycobacteria, Nocardiae and other aerobic actinomycetes, 2nd ed; approved standard CLSI document M24-A2. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, Wayne PA. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

