Is Time an Important Problem in Management of Hypertension and Hypercholesterolemia by Using an Amlodipine-Atorvastatin Single Pill Combination?
- PMID: 27459306
- PMCID: PMC4973800
- DOI: 10.12659/msm.896843
Is Time an Important Problem in Management of Hypertension and Hypercholesterolemia by Using an Amlodipine-Atorvastatin Single Pill Combination?
Abstract
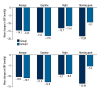
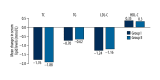
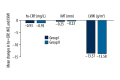
BACKGROUND Is the timing of dosing for amlodipine and atorvastatin important with regard to therapeutic efficacy? To answer this question, we designed an outpatient, practice-based, case-control study lasting 8 weeks. MATERIAL AND METHODS Two hundred patients were divided into 2 groups: in Group I, patients were provided with a single pill containing amlodipine/atorvastatin (5/20 mg) to be taken each night at 10 pm, and in Group II, patients were taking amlodipine (5 mg) and atorvastatin (20 mg) each morning at 7 am. RESULTS Our results indicated no obvious difference in blood pressure control between the 2 groups. Taking amlodipine at night not only lowered blood pressure, but it also provided better control during the peak blood pressure in the morning. Hypercholesterolemia control in the 2 groups was also not significantly different, taking atorvastatin in the morning was as effective as dosing at night in patients with hypercholesterolemia. While the carotid IMT, hs-CRP, and LVMI were significantly lower after treatment, no differences were found between the 2 groups. Although no obvious difference was found in adverse drug reactions between the 2 groups, compliance was much better in the single-pill group than in patients taking the 2 medications separately. CONCLUSIONS In conclusion, single-pill amlodipine-atorvastatin taken at night can lower blood pressure and reduce the morning peak blood pressure levels the next day. Additionally, this dosing method could improve patient adherence to the therapy.
Figures
References
-
- Liu LS Writing Group of Chinese Guidelines for the Management of H. [2010 Chinese guidelines for the management of hypertension]. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2011;39:579–615. [in Chinese] - PubMed
-
- Glorioso N, Troffa C, Filigheddu F, et al. Effect of the HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors on blood pressure in patients with essential hypertension and primary hypercholesterolemia. Hypertension. 1999;34:1281–86. - PubMed
-
- Prevention of cardiovascular events and death with pravastatin in patients with coronary heart disease and a broad range of initial cholesterol levels. The Long-Term Intervention with Pravastatin in Ischaemic Disease (LIPID) Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1998;339:1349–57. - PubMed
-
- Byington RP, Davis BR, Plehn JF, et al. Reduction of stroke events with pravastatin: the Prospective Pravastatin Pooling (PPP) Project. Circulation. 2001;103:387–92. - PubMed
-
- Schwartz GG, Olsson AG, Ezekowitz MD, et al. Myocardial Ischemia Reduction with Aggressive Cholesterol Lowering Study I. Effects of atorvastatin on early recurrent ischemic events in acute coronary syndromes: The MIRACL study: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2001;285:1711–18. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

