Role of phenolics from Spondias pinnata bark in amelioration of iron overload induced hepatic damage in Swiss albino mice
- PMID: 27459849
- PMCID: PMC4962386
- DOI: 10.1186/s40360-016-0077-6
Role of phenolics from Spondias pinnata bark in amelioration of iron overload induced hepatic damage in Swiss albino mice
Abstract
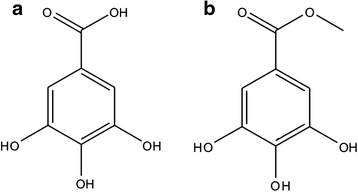
Background: Crude Spondias pinnata bark extract was previously assessed for its antioxidant, anticancer and iron chelating potentials. The isolated compounds gallic acid (GA) and methyl gallate (MG) were evaluated for their curative potential against iron overload-induced liver fibrosis and hepatocellular damage.
Methods: In vitro iron chelation property and in vivo ameliorating potential from iron overload induced liver toxicity of GA and MG was assessed by different biochemical assays and histopathological studies.
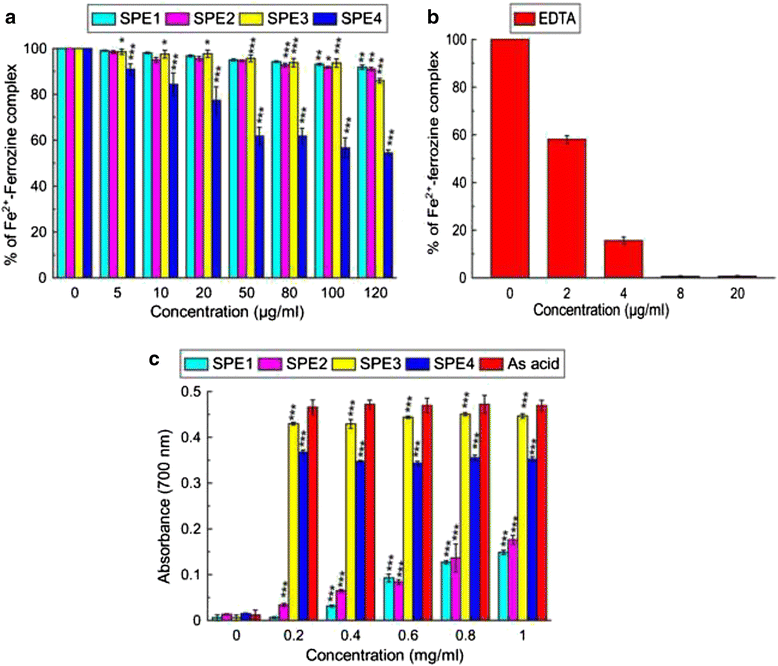
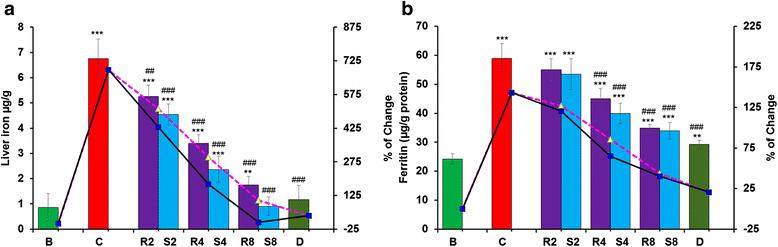
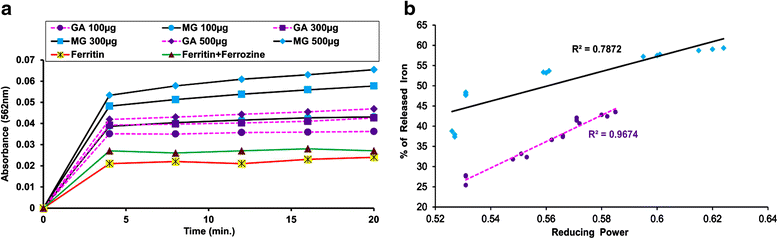
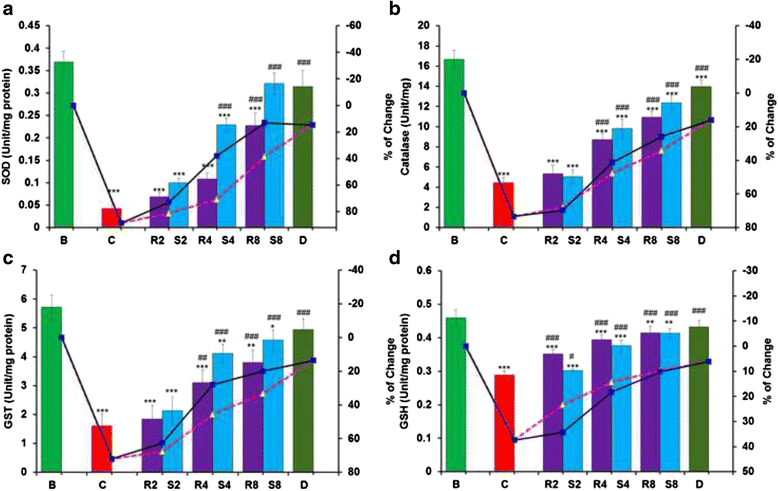
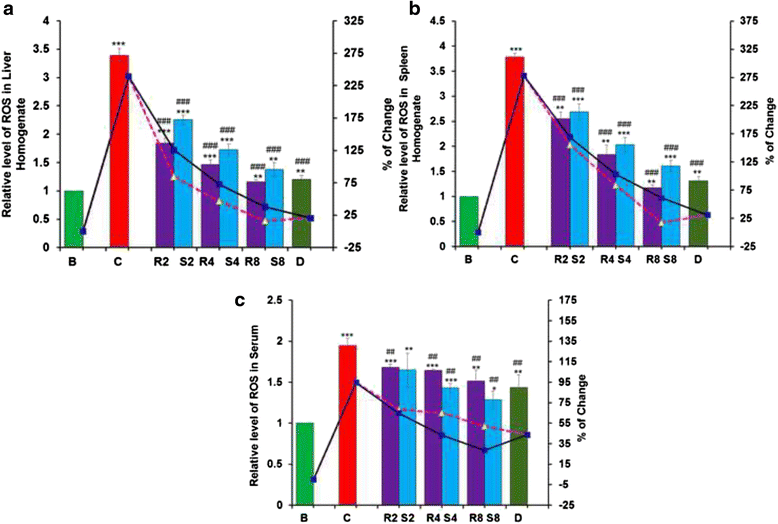
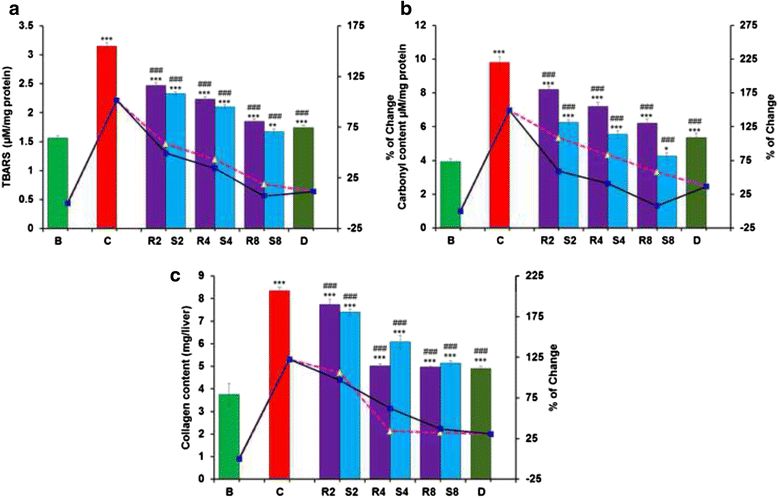
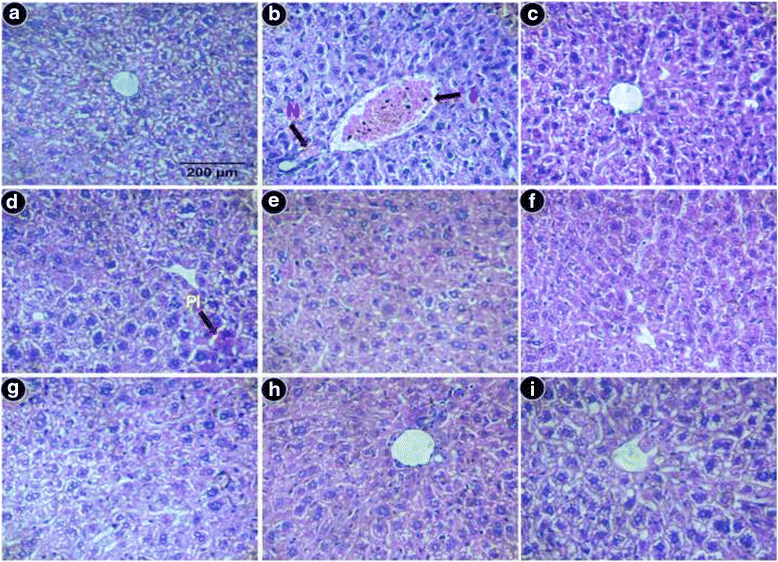
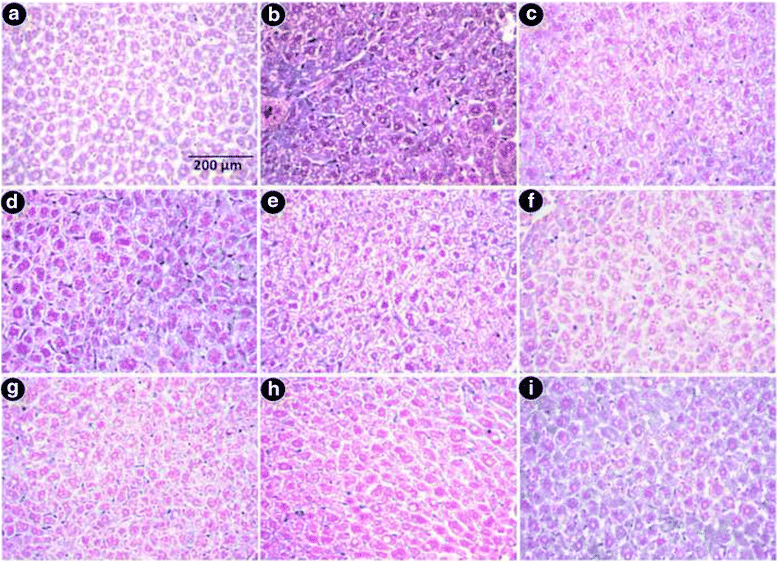
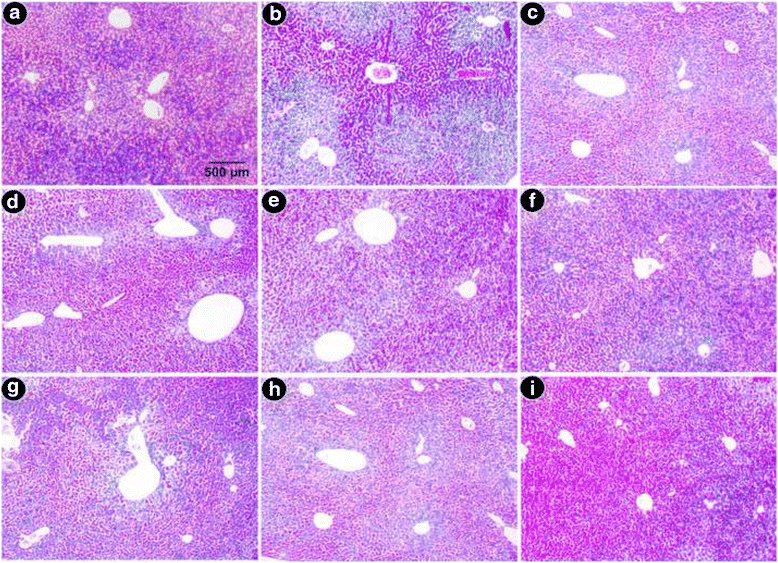
Results: MG and GA demonstrated excellent reducing power activities but iron chelation potential of MG is better than GA. Oral MG treatment in mice displayed excellent efficacy (better than GA) to significantly restore the levels of liver antioxidants, serum markers and cellular reactive oxygen species in a dose-dependent fashion. Apart from these, MG exceptionally prevented lipid peroxidation and protein oxidation whereas GA demonstrated better activity to reduce collagen content, thereby strengthening its position as an efficient drug against hepatic damage/fibrosis, which was further supported by histopathological studies. Alongside, MG efficiently eliminated the cause of liver damage, i.e., excess iron, by chelating free iron and reducing the ferritin-bound iron.
Conclusions: The present study confirmed the curative effect of GA and MG against iron overload hepatic damage via their potent antioxidant and iron-chelating potential.
Keywords: Antioxidant enzymes; Hemosiderosis; Lipid peroxidation; Liver fibrosis; Oxidative stress.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Glycoside rich fraction from Spondias pinnata bark ameliorate iron overload induced oxidative stress and hepatic damage in Swiss albino mice.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016 Jul 29;16:262. doi: 10.1186/s12906-016-1244-4. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016. PMID: 27472924 Free PMC article.
-
An ellagic acid isolated from Clerodendrum viscosum leaves ameliorates iron-overload induced hepatotoxicity in Swiss albino mice through inhibition of oxidative stress and the apoptotic pathway.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Oct;106:454-465. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.06.133. Epub 2018 Jul 11. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 29990833
-
An Indian Desert Shrub 'Hiran Chabba', Farsetia hamiltonii Royle, Exhibits Potent Antioxidant and Hepatoprotective Effect Against Iron- Overload Induced Liver Toxicity in Swiss Albino Mice.Curr Drug Discov Technol. 2019;16(2):210-222. doi: 10.2174/1570163815666180418150123. Curr Drug Discov Technol. 2019. PMID: 29669498
-
Phytochelators Intended for Clinical Use in Iron Overload, Other Diseases of Iron Imbalance and Free Radical Pathology.Molecules. 2015 Nov 23;20(11):20841-72. doi: 10.3390/molecules201119725. Molecules. 2015. PMID: 26610453 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Melatonin: Potential avenue for treating iron overload disorders.Ageing Res Rev. 2022 Nov;81:101717. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2022.101717. Epub 2022 Aug 10. Ageing Res Rev. 2022. PMID: 35961513 Review.
Cited by
-
Chemical Composition and the Cytotoxic, Antimicrobial, and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of the Fruit Peel Essential Oil from Spondias pinnata (Anacardiaceae) in Xishuangbanna, Southwest China.Molecules. 2020 Jan 15;25(2):343. doi: 10.3390/molecules25020343. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 31952118 Free PMC article.
-
Natural Antioxidants in Anemia Treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 13;22(4):1883. doi: 10.3390/ijms22041883. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33668657 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genus Spondias: A Phytochemical and Pharmacological Review.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018 Feb 12;2018:5382904. doi: 10.1155/2018/5382904. eCollection 2018. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018. PMID: 29785194 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spondias purpurea L. Bark Extract Protects against Oxidative Stress and Reduces Hypercholesterolemia in Mice Fed High-Fat Diet.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Mar 31;2022:3046483. doi: 10.1155/2022/3046483. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. Retraction in: Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2024 Jan 9;2024:9785762. doi: 10.1155/2024/9785762. PMID: 35401919 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Management of Iron Overload in Resource Poor Nations: A Systematic Review of Phlebotomy and Natural Chelators.J Toxicol. 2020 Jan 27;2020:4084538. doi: 10.1155/2020/4084538. eCollection 2020. J Toxicol. 2020. PMID: 32399029 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

