Pleuroparenchymal fibroelastosis: the prevalence of secondary forms in hematopoietic stem cell and lung transplantation recipients
- PMID: 27460284
- PMCID: PMC5019843
- DOI: 10.5152/dir.2016.15516
Pleuroparenchymal fibroelastosis: the prevalence of secondary forms in hematopoietic stem cell and lung transplantation recipients
Abstract
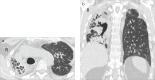
Purpose: Pleuroparenchymal fibroelastosis (PPFE) is a rare form of interstitial pneumonia, characterized by elastotic fibrosis involving the pleura and subpleural parenchyma, predominantly in the upper lobes. PPFE can be either idiopathic or secondary and mostly occurs as a late complication of lung or hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT). The aim of this study was to evaluate the prevalence of secondary forms in transplant recipients.
Methods: An expert thoracic radiologist retrospectively reviewed high-resolution computed tomography exams of 700 HSCT recipients and 53 lung transplant recipients from the database of the Radiology Department of S. Orsola-Malpighi Hospital dating back from 2007. For each case that radiologically fulfilled PPFE criteria, the following details were retrieved: clinical characteristics, laboratory and functional data, pathologic findings (obtained from one patient) and metabolic data (obtained from three patients).
Results: Six cases clinically and radiologically consistent with PPFE were identified: two HSCT recipients (0.28%) and four lung transplant recipients (7.54%).
Conclusion: In this study, PPFE was strongly associated with lung transplants as a late complication, with a prevalence of 7.54%.
Figures



References
-
- Travis WD, Costabel U, Hansell DM, et al. An official American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society statement: Update of the international multidisciplinary classification of the idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013;188:733–748. http://dx.doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201308-1483ST. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Amitani R, Niimi A, Kuse F. Idiopathic pulmonary upper lobe fibrosis (IPUF) Kokyu. 1992;11:693–699.
-
- Frankel SK, Cool CD, Lynch DA, et al. Idiopathic pleuroparenchymal fibroelastosis: description of a novel clinicopathologic entity. Chest. 2004;126:2007–2013. http://dx.doi.org/10.1378/chest.126.6.2007. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Camus P, von der Thusen J, et al. Pleuroparenchymal fibroelastosis: one more walk on the wild side of drugs? Eur Respir J. 2014;44:289–296. http://dx.doi.org/10.1183/09031936.00088414. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

