Atypical ubiquitin ligase RNF31: the nuclear factor modulator in breast cancer progression
- PMID: 27460922
- PMCID: PMC4962416
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-016-2575-8
Atypical ubiquitin ligase RNF31: the nuclear factor modulator in breast cancer progression
Abstract
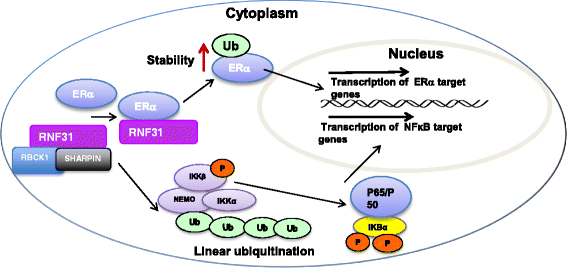
Breast cancer causes the No.1 women cancer prevalence and the No.2 women cancer mortality worldwide. Nuclear receptor/transcriptional factor signaling is aberrant and plays important roles in breast cancer pathogenesis and evolution, such as estrogen receptor α (ERα/ESR1), tumor protein p53 (p53/TP53) and Nuclear factor kappa B (NFκB). About 60-70 % of breast tumors are ERα positive, while approximate 70 % of breast tumors are P53 wild type. Recent studies indicate that nuclear receptors/transcriptional factors could be tightly controlled through protein post-translational modification.The nuclear receptors/transcriptional factors could endure several types of modifications, including phosphorylation, acetylation and ubiquitination. Compared with the other two types of modifications, ubiquitination was mostly linked to protein degradation process, while few researches focused on the functional changes of the target proteins. Until recent years, ubiquitination process is no longer regarded as merely a protein degradation process, but aslo treated as one kind of modification signal.As an atypical E3 ubiquitin ligase, RNF31 was previously found to facilitate NFκB signaling transduction through linear ubiquitination on IKKγ(IκB kinase γ). Our previous studies showed important regulatory functions of RNF31 in controlling important oncogenic pathways in breast cancer, such as ERα and p53. This review highlights recent discoveries on RNF31 functions in nuclear factor modifications, breast cancer progression and possible therapeutic inhibitors targeting RNF31.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Estrogen; RNF31; Ubiquitin ligase.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The atypical ubiquitin ligase RNF31 stabilizes estrogen receptor α and modulates estrogen-stimulated breast cancer cell proliferation.Oncogene. 2014 Aug 21;33(34):4340-51. doi: 10.1038/onc.2013.573. Epub 2014 Jan 20. Oncogene. 2014. PMID: 24441041 Free PMC article.
-
RING finger protein 31 promotes p53 degradation in breast cancer cells.Oncogene. 2016 Apr 14;35(15):1955-64. doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.260. Epub 2015 Jul 6. Oncogene. 2016. PMID: 26148235 Free PMC article.
-
Atypical ubiquitin-binding protein SHARPIN promotes breast cancer progression.Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Nov;119:109414. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109414. Epub 2019 Sep 10. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 31518875 Review.
-
Resonance assignments of the PUB domain of the RNF31 protein.Biomol NMR Assign. 2023 Dec;17(2):189-192. doi: 10.1007/s12104-023-10139-1. Epub 2023 Jul 3. Biomol NMR Assign. 2023. PMID: 37395936
-
Estrogen Receptor Alpha and its Ubiquitination in Breast Cancer Cells.Curr Drug Targets. 2019;20(6):690-704. doi: 10.2174/1389450119666181015114041. Curr Drug Targets. 2019. PMID: 30324876 Review.
Cited by
-
TRIM3 facilitates estrogen signaling and modulates breast cancer cell progression.Cell Commun Signal. 2022 Apr 7;20(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s12964-022-00861-z. Cell Commun Signal. 2022. PMID: 35392925 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of ERα Stability and Estrogen Signaling in Breast Cancer by HOIL-1.Front Oncol. 2021 May 20;11:664689. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.664689. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34094957 Free PMC article.
-
NF-κB Pathway in Autoinflammatory Diseases: Dysregulation of Protein Modifications by Ubiquitin Defines a New Category of Autoinflammatory Diseases.Front Immunol. 2017 Apr 19;8:399. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00399. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28469620 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The E3 Ubiquitin Ligase HOIP inhibits Cancer Cell Apoptosis via modulating PTEN stability.J Cancer. 2021 Sep 9;12(21):6553-6562. doi: 10.7150/jca.61996. eCollection 2021. J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34659546 Free PMC article.
-
Ubiquitin-Specific Peptidase 8 Modulates Cell Proliferation and Induces Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis in Breast Cancer by Stabilizing Estrogen Receptor Alpha.J Oncol. 2023 Jan 4;2023:8483325. doi: 10.1155/2023/8483325. eCollection 2023. J Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36644233 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vogel CL, Cobleigh MA, Tripathy D, Gutheil JC, Harris LN, Fehrenbacher L, Slamon DJ, Murphy M, Novotny WF, Burchmore M, et al. Efficacy and safety of trastuzumab as a single agent in first-line treatment of HER2-overexpressing metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20(3):719–726. doi: 10.1200/JCO.20.3.719. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Breast International Group 1-98 Collaborative G. Thurlimann B, Keshaviah A, Coates AS, Mouridsen H, Mauriac L, Forbes JF, Paridaens R, Castiglione-Gertsch M, Gelber RD, et al. A comparison of letrozole and tamoxifen in postmenopausal women with early breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2005;353(26):2747–2757. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa052258. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

