Activating transcription factor 4 underlies the pathogenesis of arsenic trioxide-mediated impairment of macrophage innate immune functions
- PMID: 27461142
- PMCID: PMC5978774
- DOI: 10.1016/j.taap.2016.07.015
Activating transcription factor 4 underlies the pathogenesis of arsenic trioxide-mediated impairment of macrophage innate immune functions
Abstract
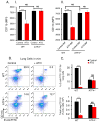
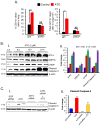
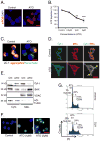
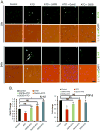
Chronic arsenic exposure to humans is considered immunosuppressive with augmented susceptibility to several infectious diseases. The exact molecular mechanisms, however, remain unknown. Earlier, we showed the involvement of unfolded protein response (UPR) signaling in arsenic-mediated impairment of macrophage functions. Here, we show that activating transcription factor 4 (ATF4), a UPR transcription factor, regulates arsenic trioxide (ATO)-mediated dysregulation of macrophage functions. In ATO-treated ATF4(+/+) wild-type mice, a significant down-regulation of CD11b expression was associated with the reduced phagocytic functions of peritoneal and lung macrophages. This severe immuno-toxicity phenotype was not observed in ATO-treated ATF4(+/-) heterozygous mice. To confirm these observations, we demonstrated in Raw 264.7 cells that ATF4 knock-down rescues ATO-mediated impairment of macrophage functions including cytokine production, bacterial engulfment and clearance of engulfed bacteria. Sustained activation of ATF4 by ATO in macrophages induces apoptosis, while diminution of ATF4 expression protects against ATO-induced apoptotic cell death. Raw 264.7 cells treated with ATO also manifest dysregulated Ca(++) homeostasis. ATO induces Ca(++)-dependent calpain-1 and caspase-12 expression which together regulated macrophage apoptosis. Additionally, apoptosis was also induced by mitochondria-regulated pathway. Restoring ATO-impaired Ca(++) homeostasis in ER/mitochondria by treatments with the inhibitors of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor (IP3R) and voltage-dependent anion channel (VDAC) attenuate innate immune functions of macrophages. These studies identify a novel role for ATF4 in underlying pathogenesis of macrophage dysregulation and immuno-toxicity of arsenic.
Keywords: ATF4; Apoptosis; Arsenic; Ca(++) homeostasis; Macrophage functions; UPR.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Ahmed S, Ahsan KB, Kippler M, Mily A, Wagatsuma Y, Hoque AM, Ngom PT, El Arifeen S, Raqib R, Vahter M. In utero arsenic exposure is associated with impaired thymic function in newborns possibly via oxidative stress and apoptosis. Toxicol Sci. 2012;129:305–314. - PubMed
-
- Aranyi C, Bradof JN, O’Shea WJ, Graham JA, Miller FJ. Effects of arsenic trioxide inhalation exposure on pulmonary antibacterial defenses in mice. J Toxicol Environ Health. 1985;15:163–172. - PubMed
-
- Attardi G, Ching E. Biogenesis of mitochondrial proteins in HeLa cells. Methods Enzymol. 1979;56:66–79. - PubMed
-
- Austyn JM, Gordon S. F4/80, a monoclonal antibody directed specifically against the mouse macrophage. Eur J Immunol. 1981;11:805–815. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

