Cost-effectiveness of hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis: A national cohort study with 14 years follow-up and matched for comorbidities and propensity score
- PMID: 27461186
- PMCID: PMC4962092
- DOI: 10.1038/srep30266
Cost-effectiveness of hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis: A national cohort study with 14 years follow-up and matched for comorbidities and propensity score
Abstract
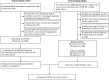
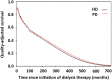
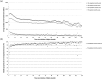
Although treatment for the dialysis population is resource intensive, a cost-effectiveness analysis comparing hemodialysis (HD) and peritoneal dialysis (PD) by matched pairs is still lacking. After matching for clinical characteristics and propensity scores, we identified 4,285 pairs of incident HD and PD patients from a Taiwanese national cohort during 1998-2010. Survival and healthcare expenditure were calculated by data of 14-year follow-up and subsequently extrapolated to lifetime estimates under the assumption of constant excess hazard. We performed a cross-sectional EQ-5D survey on 179 matched pairs of prevalent HD and PD patients of varying dialysis vintages from 12 dialysis units. The product of survival probability and the mean utility value at each time point (dialysis vintage) were summed up throughout lifetime to obtain the quality-adjusted life expectancy (QALE). The results revealed the estimated life expectancy between HD and PD were nearly equal (19.11 versus 19.08 years). The QALE's were also similar, whereas average lifetime healthcare costs were higher in HD than PD (237,795 versus 204,442 USD) and the cost-effectiveness ratios for PD and HD were 13,681 and 16,643 USD per quality-adjusted life year, respectively. In conclusion, PD is more cost-effective than HD, of which the major determinants were the costs for the dialysis modality and its associated complications.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lifetime cost-effectiveness analysis of first-line dialysis modalities for patients with end-stage renal disease under peritoneal dialysis first policy.BMC Nephrol. 2020 Feb 4;21(1):42. doi: 10.1186/s12882-020-1708-0. BMC Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 32019528 Free PMC article.
-
Cost comparison of peritoneal dialysis versus hemodialysis in end-stage renal disease.Am J Manag Care. 2009 Aug;15(8):509-18. Am J Manag Care. 2009. PMID: 19670954
-
Cost-effectiveness of haemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis for patients with end-stage renal disease in Singapore.Nephrology (Carlton). 2016 Aug;21(8):669-77. doi: 10.1111/nep.12668. Nephrology (Carlton). 2016. PMID: 26566750
-
Mortality predictor pattern in hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis in diabetic patients.Adv Clin Exp Med. 2019 Jan;28(1):133-135. doi: 10.17219/acem/76751. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2019. PMID: 30156388 Review.
-
Dialysis Modality and Mortality in the Elderly: A Meta-Analysis.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015 Jun 5;10(6):983-93. doi: 10.2215/CJN.05160514. Epub 2015 May 4. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015. PMID: 25941194 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The direct cost of chronic kidney disease (CKD) reported in Asian countries; a systematic literature review.Cost Eff Resour Alloc. 2024 Sep 5;22(1):65. doi: 10.1186/s12962-024-00566-9. Cost Eff Resour Alloc. 2024. PMID: 39237946 Free PMC article.
-
Nurse-based educational interventions in patients with peritoneal dialysis: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Int J Nurs Stud Adv. 2022 Sep 24;4:100102. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnsa.2022.100102. eCollection 2022 Dec. Int J Nurs Stud Adv. 2022. PMID: 38745642 Free PMC article.
-
Associations of Socio-Demographic, Clinical and Biochemical Parameters with Healthcare Cost, Health- and Renal-Related Quality of Life in Hemodialysis Patients: A Clinical Observational Study.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Sep 9;17(18):6552. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17186552. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32916843 Free PMC article.
-
The Intersectoral Coordination Unit for the Sustainable Intensification of Peritoneal Dialysis in Schleswig-Holstein (SKIP-SH) cohort study.BMC Nephrol. 2024 Mar 1;25(1):75. doi: 10.1186/s12882-024-03519-9. BMC Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 38429741 Free PMC article.
-
Lifetime cost-effectiveness analysis of first-line dialysis modalities for patients with end-stage renal disease under peritoneal dialysis first policy.BMC Nephrol. 2020 Feb 4;21(1):42. doi: 10.1186/s12882-020-1708-0. BMC Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 32019528 Free PMC article.
References
-
- US Renal Data System. USRDS 2014. Annual data report: atlas of chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal disease in the United States, 2014. National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, Bethesda, MD. Available at: http://www.usrds.org/2014/view/Default.aspx (Accessed: 17 August 2015).
-
- US Renal Data System. USRDS 2007. Annual data report: atlas of chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal disease in the United States, 2007. National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, Bethesda, MD. Available at: http://http://www.usrds.org/atlas07.aspx (Accessed: 17 August 2015).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

