Levodopa modulates small-world architecture of functional brain networks in Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 27461405
- PMCID: PMC5115928
- DOI: 10.1002/mds.26713
Levodopa modulates small-world architecture of functional brain networks in Parkinson's disease
Abstract
Background: PD is associated with disrupted connectivity to a large number of distributed brain regions. How the disease alters the functional topological organization of the brain, however, remains poorly understood. Furthermore, how levodopa modulates network topology in PD is largely unknown. The objective of this study was to use resting-state functional MRI and graph theory to determine how small-world architecture is altered in PD and affected by levodopa administration.
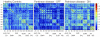
Methods: Twenty-one PD patients and 20 controls underwent functional MRI scanning. PD patients were scanned off medication and 1 hour after 200 mg levodopa. Imaging data were analyzed using 226 nodes comprising 10 intrinsic brain networks. Correlation matrices were generated for each subject and converted into cost-thresholded, binarized adjacency matrices. Cost-integrated whole-brain global and local efficiencies were compared across groups and tested for relationships with disease duration and severity.
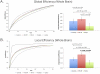
Results: Data from 2 patients and 4 controls were excluded because of excess motion. Patients off medication showed no significant changes in global efficiency and overall local efficiency, but in a subnetwork analysis did show increased local efficiency in executive (P = 0.006) and salience (P = 0.018) networks. Levodopa significantly decreased local efficiency (P = 0.039) in patients except within the subcortical network, in which it significantly increased local efficiency (P = 0.007).
Conclusions: Levodopa modulates global and local efficiency measures of small-world topology in PD, suggesting that degeneration of nigrostriatal neurons in PD may be associated with a large-scale network reorganization and that levodopa tends to normalize the disrupted network topology in PD. © 2016 International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society.
Keywords: Parkinson disease; graph theory; levodopa; resting-state fMRI.
© 2016 International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Levodopa therapy affects brain functional network dynamics in Parkinson's disease.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2025 Jan 10;136:111169. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2024.111169. Epub 2024 Oct 12. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 39401562
-
Cognitive performance in mid-stage Parkinson's disease: functional connectivity under chronic antiparkinson treatment.Brain Imaging Behav. 2019 Feb;13(1):200-209. doi: 10.1007/s11682-017-9765-0. Brain Imaging Behav. 2019. PMID: 28942477 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical pain and functional network topology in Parkinson's disease: a resting-state fMRI study.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2018 Oct;125(10):1449-1459. doi: 10.1007/s00702-018-1916-y. Epub 2018 Aug 21. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2018. PMID: 30132078 Free PMC article.
-
Global Alterations of Whole Brain Structural Connectome in Parkinson's Disease: A Meta-analysis.Neuropsychol Rev. 2023 Dec;33(4):783-802. doi: 10.1007/s11065-022-09559-y. Epub 2022 Sep 20. Neuropsychol Rev. 2023. PMID: 36125651 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuronal threshold functions: Determining symptom onset in neurological disorders.Prog Neurobiol. 2024 Nov;242:102673. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2024.102673. Epub 2024 Oct 9. Prog Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 39389338 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Altered Functional Network Connectivity of Precuneus and Executive Control Networks in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Without Cognitive Impairment.Front Neurosci. 2022 Jun 27;16:887713. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.887713. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35833084 Free PMC article.
-
Global efficiency of the motor network is decreased in Parkinson's disease in comparison with essential tremor and healthy controls.Brain Behav. 2021 Aug;11(8):e02178. doi: 10.1002/brb3.2178. Epub 2021 Jul 24. Brain Behav. 2021. PMID: 34302446 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroanatomical and Microglial Alterations in the Striatum of Levodopa-Treated, Dyskinetic Hemi-Parkinsonian Rats.Front Neurosci. 2020 Sep 15;14:567222. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2020.567222. eCollection 2020. Front Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 33041762 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Network Analysis Using Diffusion MRI Tractography in Parkinson's Disease and Correlations With Motor Impairment.Front Neurol. 2020 Sep 2;11:841. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.00841. eCollection 2020. Front Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32982909 Free PMC article.
-
A Longitudinal Randomized Controlled Trial Protocol to Evaluate the Effects of Wuqinxi on Dynamic Functional Connectivity in Parkinson's Disease Patients.Front Hum Neurosci. 2021 Sep 10;15:711703. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2021.711703. eCollection 2021. Front Hum Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34566601 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Greffard S, Verny M, Bonnet AM, et al. Motor score of the unified Parkinson disease rating scale as a good predictor of Lewy body-associated neuronal loss in the substantia Nigra. Archives of Neurology. 2006;63(4):584–588. - PubMed
-
- Prodoehl J, Burciu RG, Vaillancourt DE. Resting state functional magnetic resonance imaging in Parkinson's disease. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2014;14(6):448. - PubMed
-
- Reijneveld JC, Ponten SC, Berendse HW, Stam CJ. The application of graph theoretical analysis to complex networks in the brain. Clin Neurophysiol. 2007;118(11):2317–2331. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

