ID4 promotes AR expression and blocks tumorigenicity of PC3 prostate cancer cells
- PMID: 27462022
- PMCID: PMC4991035
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.07.092
ID4 promotes AR expression and blocks tumorigenicity of PC3 prostate cancer cells
Abstract
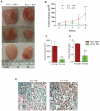
Deregulation of tumor suppressor genes is associated with tumorigenesis and the development of cancer. In prostate cancer, ID4 is epigenetically silenced and acts as a tumor suppressor. In normal prostate epithelial cells, ID4 collaborates with androgen receptor (AR) and p53 to exert its tumor suppressor activity. Previous studies have shown that ID4 promotes tumor suppressive function of AR whereas loss of ID4 results in tumor promoter activity of AR. Previous study from our lab showed that ectopic ID4 expression in DU145 attenuates proliferation and promotes AR expression suggesting that ID4 dependent AR activity is tumor suppressive. In this study, we examined the effect of ectopic expression of ID4 on highly malignant prostate cancer cell, PC3. Here we show that stable overexpression of ID4 in PC3 cells leads to increased apoptosis and decreased cell proliferation and migration. In addition, in vivo studies showed a decrease in tumor size and volume of ID4 overexpressing PC3 cells, in nude mice. At the molecular level, these changes were associated with increased androgen receptor (AR), p21, and AR dependent FKBP51 expression. At the mechanistic level, ID4 may regulate the expression or function of AR through specific but yet unknown AR co-regulators that may determine the final outcome of AR function.
Keywords: ADT; AR; Apoptosis; Cancer; FKBP51; ID4; Migration; bHLH; p21.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Inhibitor of differentiation 4 (Id4) is a potential tumor suppressor in prostate cancer.BMC Cancer. 2009 Jun 7;9:173. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-9-173. BMC Cancer. 2009. PMID: 19500415 Free PMC article.
-
Id4 deficiency attenuates prostate development and promotes PIN-like lesions by regulating androgen receptor activity and expression of NKX3.1 and PTEN.Mol Cancer. 2013 Jun 21;12:67. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-12-67. Mol Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23786676 Free PMC article.
-
Inactivation of ID4 promotes a CRPC phenotype with constitutive AR activation through FKBP52.Mol Oncol. 2017 Apr;11(4):337-357. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12028. Epub 2017 Mar 2. Mol Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28252832 Free PMC article.
-
Id4 promotes senescence and sensitivity to doxorubicin-induced apoptosis in DU145 prostate cancer cells.Anticancer Res. 2013 Oct;33(10):4271-8. Anticancer Res. 2013. PMID: 24122992 Free PMC article.
-
Non-genomic effects of the androgen receptor and vitamin D agonist are involved in suppressing invasive phenotype of prostate cancer cells.Steroids. 2006 Apr;71(4):304-9. doi: 10.1016/j.steroids.2005.09.010. Epub 2005 Nov 9. Steroids. 2006. PMID: 16289173 Review.
Cited by
-
Expression and Prognostic Value of Id-4 in Patients with Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Onco Targets Ther. 2020 Feb 12;13:1225-1234. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S230678. eCollection 2020. Onco Targets Ther. 2020. PMID: 32103990 Free PMC article.
-
The Id-protein family in developmental and cancer-associated pathways.Cell Commun Signal. 2017 Jan 25;15(1):7. doi: 10.1186/s12964-016-0161-y. Cell Commun Signal. 2017. PMID: 28122577 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Id4 Suppresses the Growth and Invasion of Colorectal Cancer HCT116 Cells through CK18-Related Inhibition of AKT and EMT Signaling.J Oncol. 2021 Apr 14;2021:6660486. doi: 10.1155/2021/6660486. eCollection 2021. J Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33936204 Free PMC article.
-
[Effect of androgen receptor on IgG expression, proliferation and migration of prostate cancer cells in vitro].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2017 Mar 20;37(3):388-392. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4254.2017.03.19. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2017. PMID: 28377358 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Use of RNA-Seq and a Transgenic Mouse Model to Identify Genes Which May Contribute to Mutant p53-Driven Prostate Cancer Initiation.Biology (Basel). 2022 Jan 29;11(2):218. doi: 10.3390/biology11020218. Biology (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35205085 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Patel D, Knowell AE, Korang-Yeboah M, Sharma P, Joshi J, Glymph S, Chinaranagari S, Nagappan P, Palaniappan R, Bowen NJ, Chaudhary J. Inhibitor of differentiation 4 (ID4) inactivation promotes de novo steroidogenesis and castration-resistant prostate cancer. Molecular endocrinology. 2014;28:1239–1253. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

