In vitro Models to Evaluate Drug-Induced Hypersensitivity: Potential Test Based on Activation of Dendritic Cells
- PMID: 27462271
- PMCID: PMC4940371
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2016.00204
In vitro Models to Evaluate Drug-Induced Hypersensitivity: Potential Test Based on Activation of Dendritic Cells
Abstract
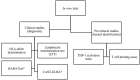
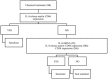
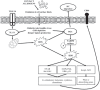
Hypersensitivity drug reactions (HDRs) are the adverse effect of pharmaceuticals that clinically resemble allergy. HDRs account for approximately 1/6 of drug-induced adverse effects, and include immune-mediated ("allergic") and non-immune-mediated ("pseudo allergic") reactions. In recent years, the severe and unpredicted drug adverse events clearly indicate that the immune system can be a critical target of drugs. Enhanced prediction in preclinical safety evaluation is, therefore, crucial. Nowadays, there are no validated in vitro or in vivo methods to screen the sensitizing potential of drugs in the pre-clinical phase. The problem of non-predictability of immunologically-based hypersensitivity reactions is related to the lack of appropriate experimental models rather than to the lack of -understanding of the adverse phenomenon. We recently established experimental conditions and markers to correctly identify drug associated with in vivo hypersensitivity reactions using THP-1 cells and IL-8 production, CD86 and CD54 expression. The proposed in vitro method benefits from a rationalistic approach with the idea that allergenic drugs share with chemical allergens common mechanisms of cell activation. This assay can be easily incorporated into drug development for hazard identification of drugs, which may have the potential to cause in vivo hypersensitivity reactions. The purpose of this review is to assess the state of the art of in vitro models to assess the allergenic potential of drugs based on the activation of dendritic cells.
Keywords: CD86; ROS; alternative methods; dendritic cell activation; drug hypersensitivity; in vitro methods.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tools to investigate and avoid drug-hypersensitivity in drug development.Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2018 May;13(5):425-433. doi: 10.1080/17460441.2018.1437141. Epub 2018 Feb 6. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2018. PMID: 29405076 Review.
-
Optimization of the THP-1 activation assay to detect pharmaceuticals with potential to cause immune mediated drug reactions.Toxicol In Vitro. 2015 Oct;29(7):1339-49. doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2015.04.012. Epub 2015 May 28. Toxicol In Vitro. 2015. PMID: 26028146
-
In vitro identification of drugs inducing systemic hypersensitivity reactions known in vivo to be associated with specific HLA genotypes.Toxicol In Vitro. 2020 Oct;68:104953. doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2020.104953. Epub 2020 Jul 28. Toxicol In Vitro. 2020. PMID: 32730864
-
The Modified THP-1 Activation Assay for the In Vitro Identification of Drug-Inducing Systemic Hypersensitivity.Front Toxicol. 2022 Mar 3;4:814050. doi: 10.3389/ftox.2022.814050. eCollection 2022. Front Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 35295210 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prediction of preservative sensitization potential using surface marker CD86 and/or CD54 expression on human cell line, THP-1.Arch Dermatol Res. 2007 Feb;298(9):427-37. doi: 10.1007/s00403-006-0714-9. Epub 2006 Nov 21. Arch Dermatol Res. 2007. PMID: 17119987
Cited by
-
Evaluation of Antineoplastic Delayed-Type Hypersensitivity Skin Reactions In Vitro.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Sep 6;15(9):1111. doi: 10.3390/ph15091111. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36145332 Free PMC article.
-
A Case of Vancomycin-Induced Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia, Systemic Symptoms and Multiorgan Involvement Proven Using Lymphocyte Transformation Test.Ann Dermatol. 2023 Apr;35(2):140-145. doi: 10.5021/ad.20.341. Ann Dermatol. 2023. PMID: 37041708 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical value of in vitro tests for the management of severe drug hypersensitivity reactions.Asia Pac Allergy. 2020 Oct 29;10(4):e44. doi: 10.5415/apallergy.2020.10.e44. eCollection 2020 Oct. Asia Pac Allergy. 2020. PMID: 33178569 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adverse immunological responses against non-viral nanoparticle (NP) delivery systems in the lung.J Immunotoxicol. 2021 Dec;18(1):61-73. doi: 10.1080/1547691X.2021.1902432. J Immunotoxicol. 2021. PMID: 33956565 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura in a Patient with Suspected COVID-19: Hydroxychloroquine Culprit or Just Happenstance?Turk J Haematol. 2021 Jun 1;38(2):155-157. doi: 10.4274/tjh.galenos.2021.2021.0057. Epub 2021 Feb 5. Turk J Haematol. 2021. PMID: 33543863 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Beeler A., Pichler W. J. (2007). In vitro tests of T-cell mediated drug hypersensitivity, in Drug Hypersensitivity, ed Pichler W. J. (Basel: Karger; ), 380–390.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

