Aliskiren Administration during Early Postnatal Life Sex-Specifically Alleviates Hypertension Programmed by Maternal High Fructose Consumption
- PMID: 27462279
- PMCID: PMC4941125
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2016.00299
Aliskiren Administration during Early Postnatal Life Sex-Specifically Alleviates Hypertension Programmed by Maternal High Fructose Consumption
Abstract
Key points summary Maternal high-fructose (HF) induces programmed hypertension in adult offspring.Early aliskiren administration prevents HF-induced hypertension in both sexes of adult offspring.HF regulates RAS components in the offspring kidney in a sex-specific manner.HF alters renal transcriptome, with female offspring being more sensitive.Deprogramming strategy to prevent hypertension might be sex-specific.
Background: Maternal high fructose (HF) intake induced renal programming and hypertension in male adult offspring. We examined whether maternal HF intake causes programmed hypertension and whether aliskiren administration confers protection against the process in a sex-specific manner, with a focus on the transcriptome changes in the kidney using next-generation RNA sequencing (NGS) technology and renin-angiotensin system (RAS).
Methods: Pregnant Sprague-Dawley rats received regular chow or chow supplemented with 60% fructose throughout pregnancy and lactation. Offspring were assigned to six groups: male control, male HF (MHF), MHF+Aliskiren, female control, female HF (FHF), and FHF+Aliskiren. Oral aliskiren 10 mg/kg/day was administered via gastric gavage between 2 and 4 weeks of age. Rats were sacrificed at 12 weeks of age.
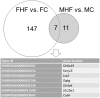
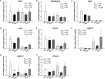
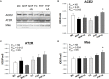
Results: Maternal HF intake induced programmed hypertension in 12-week-old offspring of both sexes. HF regulated renal transcriptome and RAS components in the offspring kidney in a sex-specific manner. Aliskiren administration prevented HF-induced programmed hypertension in both sexes of adult offspring. Aliskiren administration increased ACE2 and MAS protein levels in female kidneys exposed to maternal HF intake.
Conclusion: Maternal HF induced programmed hypertension in both sexes of adult offspring, which was sex-specifically mitigated by early aliskiren administration. Better understanding of the sex-dependent mechanisms that underlie maternal HF-induced renal programming will help develop a novel sex-specific strategy to prevent programmed hypertension.
Keywords: aliskiren; fructose; hypertension; renin-angiotensin system; sex differences.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Targeting arachidonic acid pathway to prevent programmed hypertension in maternal fructose-fed male adult rat offspring.J Nutr Biochem. 2016 Dec;38:86-92. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2016.08.006. Epub 2016 Sep 7. J Nutr Biochem. 2016. PMID: 27732913
-
High Fat Diets Sex-Specifically Affect the Renal Transcriptome and Program Obesity, Kidney Injury, and Hypertension in the Offspring.Nutrients. 2017 Apr 3;9(4):357. doi: 10.3390/nu9040357. Nutrients. 2017. PMID: 28368364 Free PMC article.
-
High salt exacerbates programmed hypertension in maternal fructose-fed male offspring.Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2015 Dec;25(12):1146-51. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2015.08.002. Epub 2015 Aug 21. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2015. PMID: 26607702
-
Maternal Fructose Intake Affects Transcriptome Changes and Programmed Hypertension in Offspring in Later Life.Nutrients. 2016 Nov 25;8(12):757. doi: 10.3390/nu8120757. Nutrients. 2016. PMID: 27897982 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Does maternal consumption of nutritive and non-nutritive sweeteners result in offspring hypertension?Front Nutr. 2025 Jan 22;12:1464269. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1464269. eCollection 2025. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 39911806 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A comprehensive guide to the pharmacologic regulation of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), the SARS-CoV-2 entry receptor.Pharmacol Ther. 2021 May;221:107750. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2020.107750. Epub 2020 Dec 1. Pharmacol Ther. 2021. PMID: 33275999 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Animal Models for Studying Developmental Origins of Cardiovascular-Kidney-Metabolic Syndrome.Biomedicines. 2025 Feb 12;13(2):452. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13020452. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40002865 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Maternal Fructose Diet-Induced Developmental Programming.Nutrients. 2021 Sep 20;13(9):3278. doi: 10.3390/nu13093278. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34579155 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System to Prevent Hypertension and Kidney Disease of Developmental Origins.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 25;22(5):2298. doi: 10.3390/ijms22052298. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33669059 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Renin-angiotensin system blockers and severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.Arch Cardiovasc Dis. 2020 Aug-Sep;113(8-9):572-578. doi: 10.1016/j.acvd.2020.07.001. Epub 2020 Aug 17. Arch Cardiovasc Dis. 2020. PMID: 32863157 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chappell M. C., Marshall A. C., Alzayadneh E. M., Shaltout H. A., Diz D. I. (2014). Update on the Angiotensin converting enzyme 2-Angiotensin (1-7)-MAS receptor axis: fetal programing, sex differences, and intracellular pathways. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 4:201. 10.3389/fendo.2013.00201 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

