Pathophysiological Mechanisms of Staphylococcus Non-aureus Bone and Joint Infection: Interspecies Homogeneity and Specific Behavior of S. pseudintermedius
- PMID: 27462303
- PMCID: PMC4940379
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.01063
Pathophysiological Mechanisms of Staphylococcus Non-aureus Bone and Joint Infection: Interspecies Homogeneity and Specific Behavior of S. pseudintermedius
Abstract
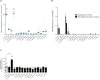
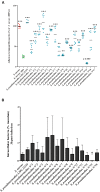
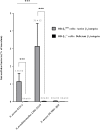
Implicated in more than 60% of bone and joint infections (BJIs), Staphylococci have a particular tropism for osteoarticular tissue and lead to difficult-to-treat clinical infections. To date, Staphylococcus aureus internalization in non-professional phagocytic cells (NPPCs) is a well-explored virulence mechanism involved in BJI chronicity. Conversely, the pathophysiological pathways associated with Staphylococcus non-aureus (SNA) BJIs have scarcely been studied despite their high prevalence. In this study, 15 reference strains from 15 different SNA species were compared in terms of (i) adhesion to human fibronectin based on adhesion microplate assays and (ii) internalization ability, intracellular persistence and cytotoxicity based on an in vitro infection model using human osteoblasts. Compared to S. aureus, S. pseudintermedius was the only species that significantly adhered to human fibronectin. This species was also associated with high (even superior to S. aureus) internalization ability, intracellular persistence and cytotoxicity. These findings were confirmed using a panel of 17 different S. pseudintermedius isolates. Additionally, S. pseudintermedius internalization by osteoblasts was completely abolished in β1 integrin-deficient murine osteoblasts. These results suggest the involvement of β1 integrin in the invasion process, although this mechanism was previously restricted to S. aureus. In summary, our results suggest that internalization into NPPCs is not a classical pathophysiologic mechanism of SNA BJIs. S. pseudintermedius appears to be an exception, and its ability to invade and subsequently induce cytotoxicity in NPPCs could explain its severe and necrotic forms of infection, notably in dogs, which exhibit a high prevalence of S. pseudintermedius infection.
Keywords: Staphylococcus non-aureus; Staphylococcus pseudintermedius; bone and joint infection (BJI); fibronectin; integrin α5β1; invasion.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification and Characterization of Staphylococcus delphini Internalization Pathway in Nonprofessional Phagocytic Cells.Infect Immun. 2020 Apr 20;88(5):e00002-20. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00002-20. Print 2020 Apr 20. Infect Immun. 2020. PMID: 32094259 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding the Virulence of Staphylococcus pseudintermedius: A Major Role of Pore-Forming Toxins.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018 Jun 28;8:221. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2018.00221. eCollection 2018. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30003063 Free PMC article.
-
More Is Not Always Better-the Double-Headed Role of Fibronectin in Staphylococcus aureus Host Cell Invasion.mBio. 2021 Oct 26;12(5):e0106221. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01062-21. Epub 2021 Oct 19. mBio. 2021. PMID: 34663090 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro antibiotic activity against intraosteoblastic Staphylococcus aureus: a narrative review of the literature.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2021 Nov 12;76(12):3091-3102. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkab301. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2021. PMID: 34459881 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Staphylococcal Adhesion and Host Cell Invasion: Fibronectin-Binding and Other Mechanisms.Front Microbiol. 2017 Dec 5;8:2433. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.02433. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 29259603 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Emerging Issues and Initial Insights into Bacterial Biofilms: From Orthopedic Infection to Metabolomics.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 Feb 13;13(2):184. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13020184. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38391570 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrating multi-wet laboratory diagnostics to study staphylococci in animals in Uganda.BMC Microbiol. 2024 Aug 10;24(1):298. doi: 10.1186/s12866-024-03442-x. BMC Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39127665 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in the Control of Clinically Important Biofilms.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 23;23(17):9526. doi: 10.3390/ijms23179526. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36076921 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Staphylococcus aureus Internalization in Osteoblast Cells: Mechanisms, Interactions and Biochemical Processes. What Did We Learn from Experimental Models?Pathogens. 2021 Feb 19;10(2):239. doi: 10.3390/pathogens10020239. Pathogens. 2021. PMID: 33669789 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of surface proteins in a clinical Staphylococcus haemolyticus isolate by bacterial surface shaving.BMC Microbiol. 2020 Apr 7;20(1):80. doi: 10.1186/s12866-020-01778-8. BMC Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32264835 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bannoehr J., Ben Zakour N. L., Reglinski M., Inglis N. F., Prabhakaran S., Fossum E., et al. (2011). Genomic and surface proteomic analysis of the canine pathogen Staphylococcus pseudintermedius reveals proteins that mediate adherence to the extracellular matrix. Infect. Immun. 79 3074–3086. 10.1128/IAI.00137-11 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Campoccia D., Testoni F., Ravaioli S., Cangini I., Maso A., Speziale P., et al. (2015). Orthopedic implant-infections. Incompetence of Staphylococcus epidermidis, Staphylococcus lugdunensis and Enterococcus faecalis to invade osteoblasts. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 10.1002/jbm.a.35564 [Epub ahead of print]. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

