Aspirin use for primary prophylaxis: Adverse outcomes in non-variceal upper gastrointestinal bleeding
- PMID: 27462392
- PMCID: PMC4942750
- DOI: 10.4240/wjgs.v8.i7.501
Aspirin use for primary prophylaxis: Adverse outcomes in non-variceal upper gastrointestinal bleeding
Abstract
Aim: To compare outcomes of patients with non-variceal upper gastrointestinal bleeding (NVUGIB) taking aspirin for primary prophylaxis to those not taking it.
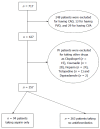
Methods: Patients not known to have any vascular disease (coronary artery or cerebrovascular disease) who were admitted to the American University of Beirut Medical Center between 1993 and 2010 with NVUGIB were included. The frequencies of in-hospital mortality, re-bleeding, severe bleeding, need for surgery or embolization, and of a composite outcome defined as the occurrence of any of the 4 bleeding related adverse outcomes were compared between patients receiving aspirin and those on no antithrombotics. We also compared frequency of in hospital complications and length of hospital stay between the two groups.
Results: Of 357 eligible patients, 94 were on aspirin and 263 patients were on no antithrombotics (control group). Patients in the aspirin group were older, the mean age was 58 years in controls and 67 years in the aspirin group (P < 0.001). Patients in the aspirin group had significantly more co-morbidities, including diabetes mellitus and hypertension [25 (27%) vs 31 (112%) and 44 (47%) vs 74 (28%) respectively, (P = 0.001)], as well as dyslipidemia [21 (22%) vs 16 (6%), P < 0.0001). Smoking was more frequent in the aspirin group [34 (41%) vs 60 (27%), P = 0.02)]. The frequencies of endoscopic therapy and surgery were similar in both groups. Patients who were on aspirin had lower in-hospital mortality rates (2.1% vs 13.7%, P = 0.002), shorter hospital stay (4.9 d vs 7 d, P = 0.01), and fewer composite outcomes (10.6% vs 24%, P = 0.01). The frequencies of in-hospital complications and re-bleeding were similar in the two groups.
Conclusion: Patients who present with NVUGIB while receiving aspirin for primary prophylaxis had fewer adverse outcomes. Thus aspirin may have a protective effect beyond its cardiovascular benefits.
Keywords: Aspirin; Morbidity; Mortality; Non-variceal upper gastrointestinal bleeding; Outcomes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Aspirin Has a Protective Effect Against Adverse Outcomes in Patients with Nonvariceal Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding.Dig Dis Sci. 2015 Jul;60(7):2077-87. doi: 10.1007/s10620-015-3604-1. Epub 2015 Mar 3. Dig Dis Sci. 2015. PMID: 25732717
-
A 13-year nationwide analysis of outcomes of non-variceal upper gastrointestinal bleeding in post-bariatric surgery patients.Transl Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025 Jan 7;10:6. doi: 10.21037/tgh-24-100. eCollection 2025. Transl Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025. PMID: 39944580 Free PMC article.
-
An observational European study on clinical outcomes associated with current management strategies for non-variceal upper gastrointestinal bleeding (ENERGIB-Turkey).Turk J Gastroenterol. 2012;23(5):463-77. doi: 10.4318/tjg.2012.0402. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2012. PMID: 23161291
-
Upper non-variceal gastrointestinal bleeding - review the effectiveness of endoscopic hemostasis methods.World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2015 Sep 25;7(13):1088-95. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v7.i13.1088. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2015. PMID: 26421105 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-variceal upper gastrointestinal bleeding.Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2018 Apr 19;4:18020. doi: 10.1038/nrdp.2018.20. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2018. PMID: 29671413 Review.
Cited by
-
Construction of a prediction model for rebleeding in patients with acute upper gastrointestinal bleeding.Eur J Med Res. 2023 Sep 15;28(1):351. doi: 10.1186/s40001-023-01349-3. Eur J Med Res. 2023. PMID: 37715244 Free PMC article.
-
An algorithmic approach to gastrointestinal bleeding in patients receiving antithrombotic agents.Gastroenterol Hepatol Bed Bench. 2020 Winter;13(Suppl1):S8-S17. Gastroenterol Hepatol Bed Bench. 2020. PMID: 33584999 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional disability after clinically significant extracranial bleeding: a secondary analysis of the Aspirin in Reducing Events in the Elderly (ASPREE) Trial.J Thromb Haemost. 2025 May;23(5):1507-1515. doi: 10.1016/j.jtha.2025.02.013. Epub 2025 Feb 20. J Thromb Haemost. 2025. PMID: 39986609 Clinical Trial.
-
Long-term aspirin use in patients hospitalized with ischemic colitis.Ann Gastroenterol. 2024 Jan-Feb;37(1):31-36. doi: 10.20524/aog.2024.0848. Epub 2023 Dec 20. Ann Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 38223253 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barada K, Abdul-Baki H, El Hajj II, Hashash JG, Green PH. Gastrointestinal bleeding in the setting of anticoagulation and antiplatelet therapy. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2009;43:5–12. - PubMed
-
- van Leerdam ME, Vreeburg EM, Rauws EA, Geraedts AA, Tijssen JG, Reitsma JB, Tytgat GN. Acute upper GI bleeding: did anything change? Time trend analysis of incidence and outcome of acute upper GI bleeding between 1993/1994 and 2000. Am J Gastroenterol. 2003;98:1494–1499. - PubMed
-
- Mose H, Larsen M, Riis A, Johnsen SP, Thomsen RW, Sørensen HT. Thirty-day mortality after peptic ulcer bleeding in hospitalized patients receiving low-dose aspirin at time of admission. Am J Geriatr Pharmacother. 2006;4:244–250. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources