Insights into the interactions between tetracycline, its degradation products and bovine serum albumin
- PMID: 27462521
- PMCID: PMC4943907
- DOI: 10.1186/s40064-016-2349-4
Insights into the interactions between tetracycline, its degradation products and bovine serum albumin
Abstract
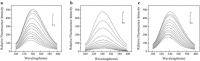
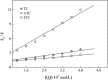
Tetracyclines (TCs) are the most widely used antibiotics in the world. Because antibiotics have low bioavailability and are difficult to completely remove using current sewage treatment facilities, residual TCs and their degradation products in the environment, animal and plant foodstuffs and personal care products may enter the body through the food chain, thus causing unpredictable effects on human health. We studied bovine serum albumin (BSA) (a functional protein) as a target of tetracycline-induced toxicity by examining its interactions with TC, anhydrotetracycline (ATC) and epitetracycline (ETC), based on a fluorescence spectroscopy and molecular docking method under simulated physiological conditions. The interaction mechanism was elucidated at the molecular level. The results show that TC, ATC and ETC bind at site II of BSA and interact mainly through hydrogen bonding interactions and van der Waals interactions. The binding affinities can be ranked in the order ATC > TC > ETC.
Keywords: BSA; Degradation products; Molecular docking; Spectroscopic method; Tetracycline.
Figures
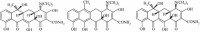



Similar articles
-
Toxic effects of tetracycline and its degradation products on freshwater green algae.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2019 Jun 15;174:43-47. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.02.063. Epub 2019 Feb 25. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2019. PMID: 30818259
-
Characterization of binding interaction of triclosan and bovine serum albumin.J Environ Sci Health A Tox Hazard Subst Environ Eng. 2020;55(3):318-325. doi: 10.1080/10934529.2019.1694346. Epub 2019 Nov 24. J Environ Sci Health A Tox Hazard Subst Environ Eng. 2020. PMID: 31762378
-
Binding of the highly toxic tetracycline derivative, anhydrotetracycline, to bovine serum albumin.Biol Pharm Bull. 2011;34(8):1301-6. doi: 10.1248/bpb.34.1301. Biol Pharm Bull. 2011. PMID: 21804222
-
The Source and Distribution of Tetracycline Antibiotics in China: A Review.Toxics. 2023 Feb 24;11(3):214. doi: 10.3390/toxics11030214. Toxics. 2023. PMID: 36976979 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microbial Degradation of Tetracycline Antibiotics: Mechanisms and Environmental Implications.J Agric Food Chem. 2024 Jun 4. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.4c02677. Online ahead of print. J Agric Food Chem. 2024. PMID: 38835142 Review.
References
-
- Daghrir R, Drogui P. Tetracycline antibiotics in the environment: a review. Environ Chem Lett. 2013;11:209–227. doi: 10.1007/s10311-013-0404-8. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

