Prognostic Value of Osteopontin Splice Variant-c Expression in Breast Cancers: A Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 27462610
- PMCID: PMC4947640
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/7310694
Prognostic Value of Osteopontin Splice Variant-c Expression in Breast Cancers: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
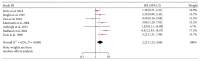
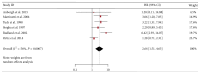
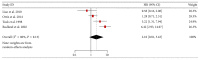
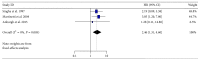
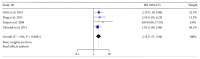
Objectives. Osteopontin (OPN) is overexpressed in breast cancers, while its clinical and prognostic significance remained unclear. This study aimed to assess the prognostic value of OPN, especially its splice variants, in breast cancers. Methods. Data were extracted from eligible studies concerning the OPN and OPN-c expression in breast cancer patients and were used to calculate the association between OPN/OPN-c and survival. Two reviewer teams independently screened the literatures according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria based on quality evaluation. Following the processes of data extraction, assessment, and transformation, meta-analysis was carried out via RevMan 5.3 software. Results. A total of ten studies involving 1,567 patients were included. The results demonstrated that high level OPN indicated a poor outcome in the OS (HR = 2.22, 95% CI: 1.23-4.00, and P = 0.008; random-effects model) with heterogeneity (I (2) = 62%) of breast cancer patients. High level OPN-c appeared to be more significantly associated with poor survival (HR = 2.14, 95% CI: 1.51-3.04, and P < 0.0001; fixed-effects model) with undetected heterogeneity (I (2) = 0%). Conclusions. Our analyses indicated that both OPN and OPN-c could be considered as prognostic markers for breast cancers. The high level of OPN-c was suggested to be more reliably associated with poor survival in breast cancer patients.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Association of osteopontin with specific prognostic factors and survival in adjuvant breast cancer trials of the Hellenic Cooperative Oncology Group.J Transl Med. 2017 Feb 13;15(1):30. doi: 10.1186/s12967-017-1134-7. J Transl Med. 2017. PMID: 28193231 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Prognostic impact of mRNA levels of osteopontin splice variants in soft tissue sarcoma patients.BMC Cancer. 2012 Apr 2;12:131. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-12-131. BMC Cancer. 2012. PMID: 22471890 Free PMC article.
-
Breast cancer risk in premalignant lesions: osteopontin splice variants indicate prognosis.Br J Cancer. 2018 Nov;119(10):1259-1266. doi: 10.1038/s41416-018-0228-1. Epub 2018 Oct 24. Br J Cancer. 2018. PMID: 30353046 Free PMC article.
-
Osteopontin splice variants and polymorphisms in cancer progression and prognosis.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2017 Aug;1868(1):93-108.A. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2017.02.005. Epub 2017 Feb 28. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28254527 Review.
-
Full-length osteopontin and its splice variants as modulators of chemoresistance and radioresistance (Review).Int J Oncol. 2019 Feb;54(2):420-430. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2018.4656. Epub 2018 Dec 6. Int J Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30535434 Review.
Cited by
-
An In Vitro Model of Mast Cell Recruitment and Activation by Breast Cancer Cells Supports Anti-Tumoral Responses.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 26;21(15):5293. doi: 10.3390/ijms21155293. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32722549 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive Biomarkers and Patient Outcome in Platinum-Resistant (PLD-Treated) Ovarian Cancer.Diagnostics (Basel). 2020 Jul 28;10(8):525. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics10080525. Diagnostics (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32731632 Free PMC article.
-
Osteopontin Mediates Cetuximab Resistance via the MAPK Pathway in NSCLC Cells.Onco Targets Ther. 2019 Nov 26;12:10177-10185. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S228437. eCollection 2019. Onco Targets Ther. 2019. PMID: 32063712 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of SPP1/osteopontin expression as predictor of recurrence in tamoxifen treated breast cancer.Sci Rep. 2020 Jan 29;10(1):1451. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-58323-w. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 31996744 Free PMC article.
-
Osteopontin at the Crossroads of Inflammation and Tumor Progression.Mediators Inflamm. 2017;2017:4049098. doi: 10.1155/2017/4049098. Epub 2017 Jul 9. Mediators Inflamm. 2017. PMID: 28769537 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Singhal H., Bautista D. S., Tonkin K. S., et al. Elevated plasma osteopontin in metastatic breast cancer associated with increased tumor burden and decreased survival. Clinical Cancer Research. 1997;3(4):605–611. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

