Circulating microRNA profiles in plasma: identification of miR-224 as a novel diagnostic biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma independent of hepatic function
- PMID: 27462777
- PMCID: PMC5288224
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.10781
Circulating microRNA profiles in plasma: identification of miR-224 as a novel diagnostic biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma independent of hepatic function
Abstract
Aims: This study was designed to identify novel microRNAs (miRNAs) in plasma for detecting and monitoring hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), independent of hepatic function and background liver diseases with different etiologies.
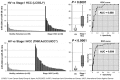
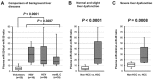
Results: (1) Four oncogenic miRNAs (miR-151, 155, 191 and 224) with high expression in HCC tissues were selected as candidates. (2) Quantitative RT-PCR using plasma samples from 107 HCC patients and 75 healthy volunteers revealed a significantly higher level of plasma miR-224 in HCC patients than in healthy volunteers according to a small-scale analysis (P < 0.0001), two independent large-scale cohort analysis (P < 0.0001, AUC 0.908). (3) miR-224 expression was significantly higher in HCC tissues and HCC cell lines than in normal hepatic tissues and fibroblasts, respectively. (P = 0.0011, 0.0150) (4) Plasma miR-224 reflected tumor dynamics; preoperative plasma levels of miR-224 were significantly reduced in postoperative samples (P = 0.0058), and plasma miR-224 levels were significantly correlated with paired miR-224 levels in HCC tissues (P = 0.0005). (5) Furthermore, plasma miR-224 levels significantly discriminated HCC patients from patients with chronic liver disease (P = 0.0008). A high plasma miR-224 level was significantly correlated with larger tumor size (P = 0.0005) and recurrences (P = 0.0027). The plasma miR-224 level could accurately detect small tumors less than 18 mm preoperatively.
Methods: We performed a systematic review of the NCBI database and selected candidate miRNAs reported as highly expressed in HCC tissue.
Conclusions: Plasma miR-224 may be a sensitive biomarker for screening HCC and monitoring tumor dynamics.
Keywords: circulating microRNA; liquid biopsy; liver cirrhosis; plasma; tumor marker.
Conflict of interest statement
We have no financial relationships to disclose.
Figures





Similar articles
-
The predictive powers of plasma trefoil factor 3 or its related micro RNAs for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2018 Nov 13;18(1):1110. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-5017-y. BMC Cancer. 2018. PMID: 30424721 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma miR-15b-5p, miR-338-5p, and miR-764 as Biomarkers for Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Med Sci Monit. 2015 Jun 29;21:1864-71. doi: 10.12659/MSM.893082. Med Sci Monit. 2015. PMID: 26119771 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatic miR-126 is a potential plasma biomarker for detection of hepatitis B virus infected hepatocellular carcinoma.Int J Cancer. 2016 Jun 1;138(11):2732-44. doi: 10.1002/ijc.29999. Epub 2016 Feb 8. Int J Cancer. 2016. PMID: 26756996
-
Circulating microRNAs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Potential Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers.Curr Pharm Des. 2016;22(34):5257-5269. doi: 10.2174/1381612822666160303110838. Curr Pharm Des. 2016. PMID: 26935703 Review.
-
Role of Circulating microRNAs in Liver Disease and HCC: Focus on miR-122.Genes (Basel). 2024 Oct 12;15(10):1313. doi: 10.3390/genes15101313. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39457437 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Epigenetic remodelling in human hepatocellular carcinoma.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022 Mar 24;41(1):107. doi: 10.1186/s13046-022-02297-2. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35331312 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serum miR-182 is a predictive biomarker for dichotomization of risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in rats.Mol Carcinog. 2019 Nov;58(11):2017-2025. doi: 10.1002/mc.23093. Epub 2019 Aug 2. Mol Carcinog. 2019. PMID: 31373075 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic Performance of microRNA-122 and microRNA-224 in Hepatitis C Virus-Induced Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC).Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2019 Aug 1;20(8):2515-2522. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2019.20.8.2515. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2019. PMID: 31450927 Free PMC article.
-
miR-224 Regulates the Aggressiveness of Hepatoma Cells Through the IL-6/STAT3/SMAD4 Pathway.Turk J Gastroenterol. 2021 Jun;32(6):532-542. doi: 10.5152/tjg.2021.191056. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2021. PMID: 34405820 Free PMC article.
-
Serum microRNA signatures and metabolomics have high diagnostic value in hepatocellular carcinoma.Oncotarget. 2017 Nov 1;8(65):108810-108824. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.22224. eCollection 2017 Dec 12. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29312570 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D, Bray F. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. International journal of cancer. 2015;136:E359–386. - PubMed
-
- Parkin DM. The global health burden of infection-associated cancers in the year 2002. International journal of cancer. 2006;118:3030–3044. - PubMed
-
- Mayans MV, Calvet X, Bruix J, Bruguera M, Costa J, Esteve J, Bosch FX, Bru C, Rodes J. Risk factors for hepatocellular carcinoma in Catalonia, Spain. International journal of cancer. 1990;46:378–381. - PubMed
-
- Donato F, Tagger A, Gelatti U, Parrinello G, Boffetta P, Albertini A, Decarli A, Trevisi P, Ribero ML, Martelli C, Porru S, Nardi G. Alcohol and hepatocellular carcinoma: the effect of lifetime intake and hepatitis virus infections in men and women. American journal of epidemiology. 2002;155:323–331. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

