New Insights into the Enterococcus faecium and Streptococcus gallolyticus subsp. gallolyticus Host Interaction Mechanisms
- PMID: 27463203
- PMCID: PMC4963119
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0159159
New Insights into the Enterococcus faecium and Streptococcus gallolyticus subsp. gallolyticus Host Interaction Mechanisms
Abstract
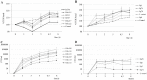
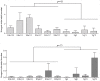
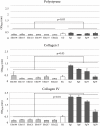
Enterococcus faecium and Streptococcus gallolyticus subsp. gallolyticus (S. gallolyticus) were classically clustered into the Lancefield Group D streptococci and despite their taxonomic reclassification still share a similar genetic content and environment. Both species are considered as opportunistic pathogens. E. faecium is often associated with nosocomial bacteraemia, and S. gallolyticus is sporadically found in endocarditis of colorectal cancer patients. In both cases, the source of infection is commonly endogenous with a translocation process that launches through the intestinal barrier. To get new insights into the pathological processes preceding infection development of both organisms, we used an in vitro model with Caco-2 cells to study and compare the adhesion, invasion and translocation inherent abilities of 6 E. faecium and 4 S. gallolyticus well-characterized isolates. Additionally, biofilm formation on polystyrene, collagen I and IV was also explored. Overall results showed that E. faecium translocated more efficiently than S. gallolyticus, inducing a destabilization of the intestinal monolayer. Isolates Efm106, Efm121 and Efm113 (p < .001 compared to Ef222) exhibited the higher translocation ability and were able to adhere 2-3 times higher than S. gallolyticus isolates. Both species preferred the collagen IV coated surfaces to form biofilm but the S. gallolyticus structures were more compact (p = .01). These results may support a relationship between biofilm formation and vegetation establishment in S. gallolyticus endocarditis, whereas the high translocation ability of E. faecium high-risk clones might partially explain the increasing number of bacteraemia.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Schleifer KH, Kilpper-Balz R. Transfer of Streptococcus faecalis and Streptococcus faecium to the genus Enterococcus nom. rev. as Enterococcus faecalis comb. nov. and Enterococcus faecium comb. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1984;34: 31–34. 10.1099/00207713-34-1-31 - DOI
-
- Kreikemeyer B, Gámez G, Margarit I, Giard JC, Hammerschmidt S, Hartke A, et al. Genomic organization, structure, regulation and pathogenic role of pilus constituents in major pathogenic Streptococci and Enterococci. International Journal of Medical Microbiology. 2011. pp. 240–251. 10.1016/j.ijmm.2010.09.003 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Weisser M, Oostdijk E a, Willems RJL, Bonten MJM, Frei R, Elzi L, et al. Dynamics of ampicillin-resistant Enterococcus faecium clones colonizing hospitalized patients: data from a prospective observational study. BMC Infect Dis. BioMed Central Ltd; 2012;12: 68 10.1186/1471-2334-12-68 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

