Assessment of whole blood thrombosis in a microfluidic device lined by fixed human endothelium
- PMID: 27464497
- PMCID: PMC4963439
- DOI: 10.1007/s10544-016-0095-6
Assessment of whole blood thrombosis in a microfluidic device lined by fixed human endothelium
Abstract
The vascular endothelium and shear stress are critical determinants of physiological hemostasis and platelet function in vivo, yet current diagnostic and monitoring devices do not fully incorporate endothelial function under flow in their assessment and, therefore, they can be unreliable and inaccurate. It is challenging to include the endothelium in assays for clinical laboratories or point-of-care settings because living cell cultures are not sufficiently robust. Here, we describe a microfluidic device that is lined by a human endothelium that is chemically fixed, but still retains its ability to modulate hemostasis under continuous flow in vitro even after few days of storage. This device lined with a fixed endothelium supports formation of platelet-rich thrombi in the presence of physiological shear, similar to a living arterial vessel. We demonstrate the potential clinical value of this device by showing that thrombus formation and platelet function can be measured within minutes using a small volume (0.5 mL) of whole blood taken from subjects receiving antiplatelet medications. The inclusion of a fixed endothelial microvessel will lead to biomimetic analytical devices that can potentially be used for diagnostics and point-of-care applications.
Keywords: Biomedical technology; Hemostasis; Lab-on-a-Chip; Platelet function tests; Thrombosis; Vascular endothelium.
Figures
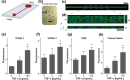
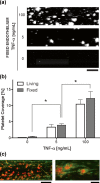
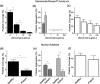
 or collagen
or collagen  as an agonist (n = 4). c Platelet coverage when blood samples containing different doses of the drug abciximab were perfused through collagen-coated microfluidic devices (n = 4). d Platelet coverage on the fixed endothelium pretreated with TNF-α when blood samples from healthy donors versus subjects treated with antiplatelet drugs were perfused through microfluidic devices (n = 11). e Light transmission aggregometry of healthy versus antiplatelet treated blood samples using ADP
as an agonist (n = 4). c Platelet coverage when blood samples containing different doses of the drug abciximab were perfused through collagen-coated microfluidic devices (n = 4). d Platelet coverage on the fixed endothelium pretreated with TNF-α when blood samples from healthy donors versus subjects treated with antiplatelet drugs were perfused through microfluidic devices (n = 11). e Light transmission aggregometry of healthy versus antiplatelet treated blood samples using ADP  or collagen
or collagen  as an agonist (n = 11). f Platelet coverage when healthy versus subject blood samples were perfused through collagen-coated microfluidic devices (n = 11). *P < 0.05
as an agonist (n = 11). f Platelet coverage when healthy versus subject blood samples were perfused through collagen-coated microfluidic devices (n = 11). *P < 0.05Similar articles
-
A microchip flow-chamber system for quantitative assessment of the platelet thrombus formation process.Microvasc Res. 2012 Mar;83(2):154-61. doi: 10.1016/j.mvr.2011.11.007. Epub 2011 Dec 6. Microvasc Res. 2012. PMID: 22166857
-
A shear gradient-activated microfluidic device for automated monitoring of whole blood haemostasis and platelet function.Nat Commun. 2016 Jan 6;7:10176. doi: 10.1038/ncomms10176. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 26733371 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a novel point-of-care device to monitor arterial thrombosis.Lab Chip. 2025 May 28;25(11):2684-2695. doi: 10.1039/d5lc00061k. Lab Chip. 2025. PMID: 40302623
-
Microfluidic technology as an emerging clinical tool to evaluate thrombosis and hemostasis.Thromb Res. 2015 Jul;136(1):13-9. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2015.05.012. Epub 2015 May 21. Thromb Res. 2015. PMID: 26014643 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Use of microfluidics to assess the platelet-based control of coagulation.Platelets. 2017 Jul;28(5):441-448. doi: 10.1080/09537104.2017.1293809. Epub 2017 Mar 30. Platelets. 2017. PMID: 28358995 Review.
Cited by
-
Formation of pressurizable hydrogel-based vascular tissue models by selective gelation in composite PDMS channels.RSC Adv. 2019 Mar 19;9(16):9136-9144. doi: 10.1039/c9ra00257j. eCollection 2019 Mar 15. RSC Adv. 2019. PMID: 35517655 Free PMC article.
-
The Biofabrication of Diseased Artery In Vitro Models.Micromachines (Basel). 2022 Feb 19;13(2):326. doi: 10.3390/mi13020326. Micromachines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35208450 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engineering "Endothelialized" Microfluidics for Investigating Vascular and Hematologic Processes Using Non-Traditional Fabrication Techniques.Curr Opin Biomed Eng. 2018 Mar;5:13-20. doi: 10.1016/j.cobme.2017.11.006. Epub 2017 Dec 5. Curr Opin Biomed Eng. 2018. PMID: 29756078 Free PMC article.
-
Engineering Organ-on-a-Chip Systems for Vascular Diseases.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2023 Dec;43(12):2241-2255. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.123.318233. Epub 2023 Oct 12. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2023. PMID: 37823265 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thrombosis-on-a-chip: Prospective impact of microphysiological models of vascular thrombosis.Curr Opin Biomed Eng. 2018 Mar;5:29-34. doi: 10.1016/j.cobme.2017.12.001. Epub 2017 Dec 18. Curr Opin Biomed Eng. 2018. PMID: 34765849 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

