The transcriptional coregulator GRIP1 controls macrophage polarization and metabolic homeostasis
- PMID: 27464507
- PMCID: PMC4974480
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms12254
The transcriptional coregulator GRIP1 controls macrophage polarization and metabolic homeostasis
Abstract
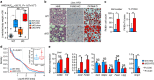
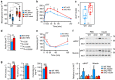
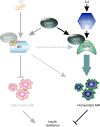
Diet-induced obesity causes chronic macrophage-driven inflammation in white adipose tissue (WAT) leading to insulin resistance. WAT macrophages, however, differ in their origin, gene expression and activities: unlike infiltrating monocyte-derived inflammatory macrophages, WAT-resident macrophages counteract inflammation and insulin resistance, yet, the mechanisms underlying their transcriptional programming remain poorly understood. We recently reported that a nuclear receptor cofactor-glucocorticoid receptor (GR)-interacting protein (GRIP)1-cooperates with GR to repress inflammatory genes. Here, we show that GRIP1 facilitates macrophage programming in response to IL4 via a GR-independent pathway by serving as a coactivator for Kruppel-like factor (KLF)4-a driver of tissue-resident macrophage differentiation. Moreover, obese mice conditionally lacking GRIP1 in macrophages develop massive macrophage infiltration and inflammation in metabolic tissues, fatty livers, hyperglycaemia and insulin resistance recapitulating metabolic disease. Thus, GRIP1 is a critical regulator of immunometabolism, which engages distinct transcriptional mechanisms to coordinate the balance between macrophage populations and ultimately promote metabolic homeostasis.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Glucocorticoid-induced phosphorylation by CDK9 modulates the coactivator functions of transcriptional cofactor GRIP1 in macrophages.Nat Commun. 2017 Nov 23;8(1):1739. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-01569-2. Nat Commun. 2017. PMID: 29170386 Free PMC article.
-
Deficiency of Cbl-b gene enhances infiltration and activation of macrophages in adipose tissue and causes peripheral insulin resistance in mice.Diabetes. 2007 Oct;56(10):2511-22. doi: 10.2337/db06-1768. Epub 2007 Jun 29. Diabetes. 2007. PMID: 17601987
-
SGLT2 Inhibition by Empagliflozin Promotes Fat Utilization and Browning and Attenuates Inflammation and Insulin Resistance by Polarizing M2 Macrophages in Diet-induced Obese Mice.EBioMedicine. 2017 Jun;20:137-149. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2017.05.028. Epub 2017 May 26. EBioMedicine. 2017. PMID: 28579299 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic influence on macrophage polarization and pathogenesis.BMB Rep. 2019 Jun;52(6):360-372. doi: 10.5483/BMBRep.2019.52.6.140. BMB Rep. 2019. PMID: 31186085 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aggressive Crosstalk Between Fatty Acids and Inflammation in Macrophages and Their Influence on Metabolic Homeostasis.Neurochem Res. 2018 Jan;43(1):19-26. doi: 10.1007/s11064-017-2269-x. Epub 2017 Apr 19. Neurochem Res. 2018. PMID: 28424949 Review.
Cited by
-
HNF4A mitigates sepsis-associated lung injury by upregulating NCOR2/GR/STAB1 axis and promoting macrophage polarization towards M2 phenotype.Cell Death Dis. 2025 Feb 21;16(1):120. doi: 10.1038/s41419-025-07452-z. Cell Death Dis. 2025. PMID: 39979267 Free PMC article.
-
Status of M1 and M2 type macrophages in keloid.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2017 Nov 1;10(11):11098-11105. eCollection 2017. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2017. PMID: 31966458 Free PMC article.
-
Typically inhibiting USP14 promotes autophagy in M1-like macrophages and alleviates CLP-induced sepsis.Cell Death Dis. 2020 Aug 20;11(8):666. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-02898-9. Cell Death Dis. 2020. PMID: 32820146 Free PMC article.
-
Physiological Convergence and Antagonism Between GR and PPARγ in Inflammation and Metabolism.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022;1390:123-141. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-11836-4_7. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022. PMID: 36107316 Review.
-
Regulations of Glycolytic Activities on Macrophages Functions in Tumor and Infectious Inflammation.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020 Jun 12;10:287. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00287. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32596169 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wensveen F. M., Valentic S., Sestan M., Turk Wensveen T. & Polic B. The ‘Big Bang' in obese fat: events initiating obesity-induced adipose tissue inflammation. Eur. J. Immunol. 45, 2446–2456 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Olefsky J. M. & Glass C. K. Macrophages, inflammation, and insulin resistance. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 72, 219–246 (2010). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

