Normative Hearing Threshold Levels in Koreans with Normal Tympanic Membranes and Estimated Prevalence of Hearing Loss
- PMID: 27464516
- PMCID: PMC5426397
- DOI: 10.21053/ceo.2016.00031
Normative Hearing Threshold Levels in Koreans with Normal Tympanic Membranes and Estimated Prevalence of Hearing Loss
Abstract
Objectives: We investigated the normative data on the hearing threshold levels of Koreans with normal tympanic membranes and the prevalence of hearing loss (HL) and nonserviceable hearing using the data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (KNHANES) during 2010-2012.
Methods: Data obtained from 16,673 participants ≥12-year-of-age with normal tympanic membranes who completed audiometric testing. We defined HL as the pure tone average (PTA) >25 dB hearing level at 500, 1,000, 2,000, and 3,000 Hz and non-serviceable hearing as PTA >40 dB hearing level.
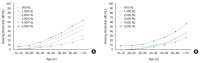
Results: The hearing levels at some frequencies (0.5, 3, and 6 kHz) did not differ in between the 10's and 20's, but the hearing thresholds at all frequencies increased gradually from the 30's. The hearing thresholds were higher in men than in women at high frequencies (3, 4, and 6 kHz) in the 30's and older. The prevalence of HL in either ear was 16.5% (estimates of 5.9 million), from 2.4% in the 10's up to 75.4% in the 70's and older. The prevalence of nonserviceable hearing in either ear was 6.8% (estimates of 2.5 million) and that of bilateral nonserviceable hearing was 2.5% (estimates of 0.9 million).
Conclusion: Hearing loss aggravated from the 30's at all frequencies and men showed poorer hearing levels than women at high frequencies. Hearing loss was a common condition and the prevalence of non-serviceable hearing in either ear, which needs hearing rehabilitation to help social communication, was 6.8%. Normative pure tone thresholds at each frequency can be used as referent values when counseling patients complaining of hearing loss.
Keywords: Audiometry; Hearing Loss; Normative Data; Pure Tone; Thresholds.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Otitis media with effusion in children: Cross-frequency correlation in pure tone audiometry.PLoS One. 2019 Aug 22;14(8):e0221405. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0221405. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31437206 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of Hearing Loss Among a Representative Sample of Canadian Children and Adolescents, 3 to 19 Years of Age.Ear Hear. 2017 Jan/Feb;38(1):7-20. doi: 10.1097/AUD.0000000000000345. Ear Hear. 2017. PMID: 27556530 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of cochlear hearing disorders: normative distortion product otoacoustic emission measurements.Ear Hear. 2007 Dec;28(6):778-92. doi: 10.1097/AUD.0b013e3181576755. Ear Hear. 2007. PMID: 17982366
-
Intratympanic dexamethasone for sudden sensorineural hearing loss after failure of systemic therapy.Laryngoscope. 2007 Jan;117(1):3-15. doi: 10.1097/01.mlg.0000245058.11866.15. Laryngoscope. 2007. PMID: 17202923 Review.
-
Pure Tone Audiometry and Hearing Loss in Alzheimer's Disease: A Meta-Analysis.Front Psychol. 2022 Jan 21;12:788045. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.788045. eCollection 2021. Front Psychol. 2022. PMID: 35153910 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Is sleep apnea truly associated with hearing loss? A nationwide, population-based study with STOP-BANG questionnaire.Front Public Health. 2023 May 25;11:1170470. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1170470. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37333523 Free PMC article.
-
Speech-in-Noise Test results of compensation claimants for noise induced hearing loss in Korean male workers: Words-in-Noise Test (WIN) and quick-Hearing-in-Noise Test (HINT).Ann Occup Environ Med. 2021 Apr 20;33:e11. doi: 10.35371/aoem.2021.33.e11. eCollection 2021. Ann Occup Environ Med. 2021. PMID: 34754472 Free PMC article.
-
Revisiting Age-Related Normative Hearing Levels in Korea.J Korean Med Sci. 2025 Jan 13;40(2):e3. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2025.40.e3. J Korean Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 39807003 Free PMC article.
-
Foreign Body Complications in Ears due to Mishandled Hearing Aid Fitting and Proposed Clinical Guidelines to Address the Complications.J Korean Med Sci. 2022 Jan 10;37(2):e19. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2022.37.e19. J Korean Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 35014230 Free PMC article.
-
Robust and Efficient Online Auditory Psychophysics.Trends Hear. 2022 Jan-Dec;26:23312165221118792. doi: 10.1177/23312165221118792. Trends Hear. 2022. PMID: 36131515 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cooper JC., Jr Health and Nutrition Examination Survey of 1971-75: part I. ear and race effects in hearing. J Am Acad Audiol. 1994 Jan;5(1):30–6. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

