Identification and characterization of Xenopus tropicalis common progenitors of Sertoli and peritubular myoid cell lineages
- PMID: 27464670
- PMCID: PMC5051652
- DOI: 10.1242/bio.019265
Identification and characterization of Xenopus tropicalis common progenitors of Sertoli and peritubular myoid cell lineages
Abstract
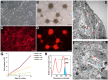
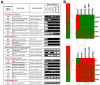
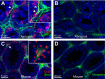
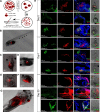
The origin of somatic cell lineages during testicular development is controversial in mammals. Employing basal amphibian tetrapod Xenopus tropicalis we established a cell culture derived from testes of juvenile male. Expression analysis showed transcription of some pluripotency genes and Sertoli cell, peritubular myoid cell and mesenchymal cell markers. Transcription of germline-specific genes was downregulated. Immunocytochemistry revealed that a majority of cells express vimentin and co-express Sox9 and smooth muscle α-actin (Sma), indicating the existence of a common progenitor of Sertoli and peritubular myoid cell lineages. Microinjection of transgenic, red fluorescent protein (RFP)-positive somatic testicular cells into the peritoneal cavity of X. tropicalis tadpoles resulted in cell deposits in heart, pronephros and intestine, and later in a strong proliferation and formation of cell-to-cell net growing through the tadpole body. Immunohistochemistry analysis of transplanted tadpoles showed a strong expression of vimentin in RFP-positive cells. No co-localization of Sox9 and Sma signals was observed during the first three weeks indicating their dedifferentiation to migratory-active mesenchymal cells recently described in human testicular biopsies.
Keywords: Common progenitor; Migration potential; Testicular somatic cells; Xenopus tropicalis.
© 2016. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures

References
-
- Berndtson W. E. and Thompson T. L. (1990). Changing relationships between testis size, Sertoli cell number and spermatogenesis in Sprague-Dawley rats. J. Androl. 11, 429-435. - PubMed
-
- Bott R., McFee R., Clopton D., Toombs C. and Cupp A. (2006). Vascular endothelial growth factor and kinase domain region receptor are involved in both seminiferous cord formation and vascular development during testis morphogenesis in the rat. Biol. Reprod. 75, 56-67. 10.1095/biolreprod.105.047225 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

