A preliminary exploration of ulnar variance in healthy wrists at a tertiary hospital in Jeddah
- PMID: 27464859
- PMCID: PMC5018699
- DOI: 10.15537/smj.2016.8.14144
A preliminary exploration of ulnar variance in healthy wrists at a tertiary hospital in Jeddah
Abstract
Objectives: To gain preliminary insight by exploring ulnar variance changes in a Saudi-based sample.
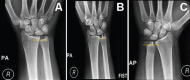
Methods: This 6-month (December 2013 to June 2014) cross-sectional study was conducted on a randomly selected healthy adult volunteers with a sample size of 104, at King Abdulaziz University Hospital, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. Posteroanterior (PA), anteroposterior (AP), and PA grip views are taken. The variables of interest were the PA, AP, and PA fist measurements of both right and left wrists. An independent t-test was used to compare means between groups.
Results: A total of 104 volunteers were recruited. Among 17 participants who had a negative ulnar variance on right PA views, a significantly high proportion (n=9; 56.2%) maintained a negative value on fist views; 7 participants (43.8%) had a neutral ulnar variance while none (0%) had a positive value (p less than 0.001). Similarly, a significant proportion of participants who had neutral, or positive values on right PA views maintained the same values on right fist views (p less than 0.001). On radiographs of the right wrist, the ulnar variance decreased with a change in wrist position, with an absolute difference in magnitude of 2.13 (p less than 0.001) between PA and AP views. Similarly, the ulnar variance on the left side decreased significantly between PA and AP views (absolute difference in magnitude, 1.68; p less than 0.001).
Conclusions: Ulnar variance changes in our sample are similar to what is reported in the literature.
Figures
References
-
- Afshar A, Aminzadeh-Gohari A, Yekta Z. The association of Kienbock’s disease and ulnar variance in the Iranian population. J Hand Surg Eur. 2013;38:496–499. - PubMed
-
- Ng CY, McQueen MM. What are the radiological predictors of functional outcome following fractures of the distal radius? J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2011;93:145–150. - PubMed
-
- Laino DK, Petchprapa CN, Lee SK. Ulnar variance: correlation of plain radiographs, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging with anatomic dissection. J Hand Surg Am. 2012;37:90–97. - PubMed
-
- Amaral L, Claessens AL, Ferreirinha J, Maia J, Santos P. Does ulnar variance change with age and what is the influence of training and biological characteristics in this change?A short-term longitudinal study in Portuguese artistic gymnasts. Clin J Sport Med. 2014;24:429–434. - PubMed
-
- Goldfarb CA, Strauss NL, Wall LB, Calfee RP. Defining ulnar variance in the adolescent wrist: measurement technique and interobserver reliability. J Hand Surg Am. 2011;36:272–277. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

