Randomised clinical study: inulin short-chain fatty acid esters for targeted delivery of short-chain fatty acids to the human colon
- PMID: 27464984
- PMCID: PMC5026196
- DOI: 10.1111/apt.13749
Randomised clinical study: inulin short-chain fatty acid esters for targeted delivery of short-chain fatty acids to the human colon
Abstract
Background: Short-chain fatty acids (SCFA) produced through fermentation of nondigestible carbohydrates by the gut microbiota are associated with positive metabolic effects. However, well-controlled trials are limited in humans.
Aims: To develop a methodology to deliver SCFA directly to the colon, and to optimise colonic propionate delivery in humans, to determine its role in appetite regulation and food intake.
Methods: Inulin SCFA esters were developed and tested as site-specific delivery vehicles for SCFA to the proximal colon. Inulin propionate esters containing 0-61 wt% (IPE-0-IPE-61) propionate were assessed in vitro using batch faecal fermentations. In a randomised, controlled, crossover study, with inulin as control, ad libitum food intake (kcal) was compared after 7 days on IPE-27 or IPE-54 (10 g/day all treatments). Propionate release was determined using (13) C-labelled IPE variants.
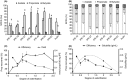
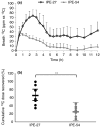
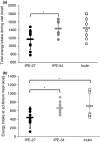
Results: In vitro, IPE-27-IPE-54 wt% propionate resulted in a sevenfold increase in propionate production compared with inulin (P < 0.05). In vivo, IPE-27 led to greater (13) C recovery in breath CO2 than IPE-54 (64.9 vs. 24.9%, P = 0.001). IPE-27 also led to a reduction in energy intake during the ad libitum test meal compared with both inulin (439.5 vs. 703.9 kcal, P = 0.025) and IPE-54 (439.5 vs. 659.3 kcal, P = 0.025), whereas IPE-54 was not significantly different from inulin control.
Conclusions: IPE-27 significantly reduced food intake suggesting colonic propionate plays a role in appetite regulation. Inulin short-chain fatty acid esters provide a novel tool for probing the diet-gut microbiome-host metabolism axis in humans.
© 2016 The Authors. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- De Vadder F, Kovatcheva‐Datchary P, Goncalves D, et al Microbiota‐generated metabolites promote metabolic benefits via gut‐brain neural circuits. Cell 2014; 156: 84–96. - PubMed
-
- Trompette A, Gollwitzer ES, Yadava K, et al Gut microbiota metabolism of dietary fiber influences allergic airway disease and hematopoiesis. Nat Med 2014; 20: 159–66. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- BB/H532075/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/H532091/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/L004259/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/H005072/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/H004815/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
