Immune pathogenesis of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia
- PMID: 27465274
- PMCID: PMC6260829
- DOI: 10.1160/TH16-01-0074
Immune pathogenesis of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia
Abstract
The immune response to heparin is one of the most common drug-induced allergies, and yet, atypical for a drug hypersensitivity reaction. Whereas most drug-induced allergies are rare, idiosyncratic and life-long, the allergic response to heparin is common, predictable in certain clinical settings and transient. Advances in the last decade with regards to structural characterisation of the PF4/heparin antigenic complex, contributions of innate immunity and development of animal models have provided insights into the distinctive features of the HIT immune response. Recent descriptions of the crystal structure of the PF4/heparin complex, alongside other biophysical studies, have clarified the structural requirements for immunogenicity and heparin-dependency of antibody formation. Studies of interactions of PF4 with bacterial cell walls as well as epidemiologic associations of anti-PF4/heparin antibody formation and infection suggest a role for immune priming and explain the rapid evolution of an isotype-switched immune response in sensitised patients. Murine models have greatly facilitated investigations of cellular basis of the HIT response and identified a major role for T-cells and marginal zone B-cells, but key findings have yet to be validated in human disease. This chapter will summarise recent investigations of the HIT immune response in the context of major pathways of immune activation and identify areas of uncertainty.
Keywords: Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia; heparin; murine models; platelet factor 4.
Figures
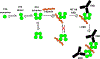
Similar articles
-
Evolving concepts of pathogenesis of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia: Diagnostic and therapeutic implications.Int J Lab Hematol. 2020 Jun;42 Suppl 1:25-32. doi: 10.1111/ijlh.13223. Int J Lab Hematol. 2020. PMID: 32543064 Review.
-
Further insights into the anti-PF4/heparin IgM immune response.Thromb Haemost. 2016 Apr;115(4):752-61. doi: 10.1160/TH15-08-0654. Epub 2015 Oct 15. Thromb Haemost. 2016. PMID: 26467272
-
Critical role for mouse marginal zone B cells in PF4/heparin antibody production.Blood. 2013 Apr 25;121(17):3484-92. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-01-477091. Epub 2013 Mar 4. Blood. 2013. PMID: 23460609 Free PMC article.
-
Studies of the anti-platelet factor 4/heparin immune response: adapting the enzyme-linked immunosorbent spot assay for detection of memory B cells against complex antigens.Transfusion. 2010 Jan;50(1):32-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1537-2995.2009.02360.x. Epub 2009 Aug 26. Transfusion. 2010. PMID: 19709391
-
Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia: an autoimmune disorder regulated through dynamic autoantigen assembly/disassembly.J Clin Apher. 2007 Feb;22(1):31-6. doi: 10.1002/jca.20109. J Clin Apher. 2007. PMID: 17285619 Review.
Cited by
-
Combination of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Low-Molecular-Weight Heparin Prevents Deep Vein Thrombosis After Surgery: A Meta-Analysis.Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2019 Jan-Dec;25:1076029619890411. doi: 10.1177/1076029619890411. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2019. PMID: 31867999 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Human Leukocyte Antigen (HLA) Alleles and Killer Cell Immunoglobulin-Like Receptors (KIR) Types on Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia (HIT).Pharmacotherapy. 2017 Sep;37(9):1164-1171. doi: 10.1002/phar.1983. Epub 2017 Sep 4. Pharmacotherapy. 2017. PMID: 28688202 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in hydrogels for capturing and neutralizing inflammatory cytokines.J Tissue Eng. 2025 Jun 25;16:20417314251342175. doi: 10.1177/20417314251342175. eCollection 2025 Jan-Dec. J Tissue Eng. 2025. PMID: 40575355 Free PMC article. Review.
-
To clot or not to clot? Ad is the question-Insights on mechanisms related to vaccine-induced thrombotic thrombocytopenia.J Thromb Haemost. 2021 Nov;19(11):2845-2856. doi: 10.1111/jth.15485. Epub 2021 Aug 23. J Thromb Haemost. 2021. PMID: 34351057 Free PMC article.
-
Temporality of heparin-induced antibodies: a retrospective study in outpatients undergoing hemodialysis on unfractionated heparin.Exp Hematol Oncol. 2018 Sep 14;7:23. doi: 10.1186/s40164-018-0115-8. eCollection 2018. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30221035 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Krauel K, Potschke C, Weber C, et al. Platelet factor 4 binds to bacteria, inducing antibodies cross-reacting with the major antigen in heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Blood 2011; 117: 1370–1378. - PubMed
-
- Warkentin TE, Makris M, Jay RM, et al. A Spontaneous Prothrombotic Disorder Resembling Heparin-induced Thrombocytopenia. Amer J Med 2008; 121: 632–636. - PubMed
-
- Jay RM, Warkentin TE. Fatal heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) during warfarin thromboprophylaxis following orthopedic surgery: another example of ‘spontaneous’ HIT? J Thromb Haemost 2008; 6: 1598–1600. - PubMed
-
- Warkentin TE, Basciano PA, Knopman J, et al. Spontaneous heparin-induced thrombocytopenia syndrome: 2 new cases and a proposal for defining this disorder. Blood 2014; 123: 3651–3654. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

