Biochemical Activities and Genetic Functions of the Drosophila melanogaster Fancm Helicase in DNA Repair
- PMID: 27466228
- PMCID: PMC5068844
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.116.192534
Biochemical Activities and Genetic Functions of the Drosophila melanogaster Fancm Helicase in DNA Repair
Abstract
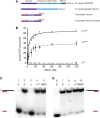
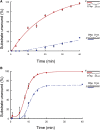
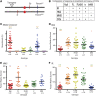
Repair of DNA damage is essential to the preservation of genomic stability. During repair of double-strand breaks, several helicases function to promote accurate repair and prevent the formation of crossovers through homologous recombination. Among these helicases is the Fanconi anemia group M (FANCM) protein. FANCM is important in the response to various types of DNA damage and has been suggested to prevent mitotic crossovers during double-strand break repair. The helicase activity of FANCM is believed to be important in these functions, but no helicase activity has been detected in vitro We report here a genetic and biochemical study of Drosophila melanogaster Fancm. We show that purified Fancm is a 3' to 5' ATP-dependent helicase that can disassemble recombination intermediates, but only through limited lengths of duplex DNA. Using transgenic flies expressing full-length or truncated Fancm, each with either a wild-type or mutated helicase domain, we found that there are helicase-independent and C-terminal-independent functions in responding to DNA damage and in preventing mitotic crossovers.
Keywords: ATP activity; DNA helicase; biochemistry; crossing over; genetics; homologous recombination; synthesis-dependent strand annealing.
Copyright © 2016 by the Genetics Society of America.
Figures

References
-
- Adams M. D., McVey M., Sekelsky J., 2003. Drosophila BLM in double-strand break repair by synthesis-dependent strand annealing. Science 299: 265–267. - PubMed
-
- Ciccia A., Ling C., Coulthard R., Yan Z., Xue Y., et al. , 2007. Identification of FAAP24, a Fanconi anemia core complex protein that interacts with FANCM. Mol. Cell 25: 331–343. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

