FOLFIRINOX for advanced pancreatic cancer: the Princess Margaret Cancer Centre experience
- PMID: 27467054
- PMCID: PMC5023770
- DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2016.222
FOLFIRINOX for advanced pancreatic cancer: the Princess Margaret Cancer Centre experience
Abstract
Background: FOLFIRINOX has been shown to significantly increase both overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) in metastatic pancreas cancer. There is limited data regarding the treatment of locally advanced pancreatic cancer. We present a retrospective study of patients with both locally advanced and metastatic pancreas cancer using FOLFIRINOX as first-line therapy in our centre.
Methods: This is a retrospective review of patients treated with FOLFIRINOX for pancreatic cancer at Princess Margaret Cancer Centre, between December 2011 and July 2014. The primary objective was to evaluate the efficacy and safety of FOLFIRINOX when used with dose modifications.
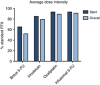
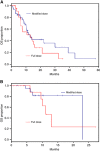
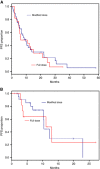
Results: One hundred two patients were identified; 66 metastatic and 36 locally advanced. Sixty-eight per cent of patients initiated treatment with a dose reduction. The median (95% CI) OS in the metastatic group was 13.1 (6.3-16.1) months with full dose and 12.9 (10.3-30.1) months with modified dose. The median (95% CI) OS in the locally advanced group was 11.1 (6.1-not reached) months with full dose and 23 (not reached-not reached) months with modified dose. The median (95% CI) PFS in the metastatic group was 6.2 (4.9-15.2) months with full dose and 8.7 (5.7-12.9) months with modified dose. The median (95% CI) PFS in the locally advanced group was 11.1 (3.1-not reached) months with full dose and 10.4 (6.8-not reached) months with modified dose. Grade 3/4 haematologic adverse events were observed in 43% of patients. Grade 3/4 non-haematologic adverse events were observed in 28% of patients. Patient well-being significantly improved from baseline to cycle 4 (P=0.002).
Conclusions: Efficacy was achievable with dose-modified FOLFIRINOX in daily setting. The safety of FOLFIRINOX remains a concern with a high rate of grades 3 and 4 neutropaenia despite dose reduction.
Figures
Similar articles
-
5-Fluorouracil/leucovorin combined with irinotecan and oxaliplatin (FOLFIRINOX) as second-line chemotherapy in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer who have progressed on gemcitabine-based therapy.Chemotherapy. 2013;59(4):273-9. doi: 10.1159/000356158. Epub 2014 Jan 18. Chemotherapy. 2013. PMID: 24457620
-
Sustained response with gemcitabine plus Nab-paclitaxel after folfirinox failure in metastatic pancreatic cancer: report of an effective new strategy.Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2014 Apr;38(2):e23-6. doi: 10.1016/j.clinre.2014.01.005. Epub 2014 Feb 18. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 24559766
-
Safety and tolerability of the first-in-class agent CPI-613 in combination with modified FOLFIRINOX in patients with metastatic pancreatic cancer: a single-centre, open-label, dose-escalation, phase 1 trial.Lancet Oncol. 2017 Jun;18(6):770-778. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30314-5. Epub 2017 May 8. Lancet Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28495639 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
FOLFIRINOX for locally advanced and metastatic pancreatic cancer: single institution retrospective review of efficacy and toxicity.Med Oncol. 2013 Mar;30(1):361. doi: 10.1007/s12032-012-0361-2. Epub 2012 Dec 28. Med Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23271209 Review.
-
Current Standard and Future Perspectives in First- and Second-Line Treatment of Metastatic Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma.Digestion. 2016;94(1):44-9. doi: 10.1159/000447739. Epub 2016 Jul 21. Digestion. 2016. PMID: 27438590 Review.
Cited by
-
A real-world analysis of nanoliposomal-irinotecan with 5-fluorouracil and folinic acid as third- or later-line therapy in patients with metastatic pancreatic adenocarcinoma.Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2022 Aug 29;14:17588359221119539. doi: 10.1177/17588359221119539. eCollection 2022. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36062047 Free PMC article.
-
The benefits of modified FOLFIRINOX for advanced pancreatic cancer and its induced adverse events: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Sci Rep. 2018 Jun 6;8(1):8666. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-26811-9. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29875415 Free PMC article.
-
Patient-tailored FOLFIRINOX as first line treatment of patients with advanced pancreatic adenocarcinoma.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Apr;98(16):e15341. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000015341. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 31008993 Free PMC article.
-
Phase IB/II Randomized Study of FOLFIRINOX Plus Pegylated Recombinant Human Hyaluronidase Versus FOLFIRINOX Alone in Patients With Metastatic Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma: SWOG S1313.J Clin Oncol. 2019 May 1;37(13):1062-1069. doi: 10.1200/JCO.18.01295. Epub 2019 Feb 28. J Clin Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30817250 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of efficacy and safety between standard-dose and modified-dose FOLFIRINOX as a first-line treatment of pancreatic cancer.World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2018 Nov 15;10(11):421-430. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v10.i11.421. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30487953 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amirealut C, Beaudet J, Gaudet G, Raymond N, Ayoub J-PM, Letourneau R, Loungnarath R, Tehfe MA, Aubin F (2014) FOLFIRINOX in the real world setting: the multicentric experience of six Canadian Institutions. J Clin Oncol 32(suppl 3): abstract 367.
-
- Blazer M, Wu C, Goldberg RM, Phillips G, Schmidt C, Muscarella P, Wuthrick E, Williams TM, Reardon J, Ellison EC, Bloomston M, Bekaii-Saab T (2015) Neoadjuvant modified (m) FOLFIRINOX for locally advanced unresectable (LAPC) and borderline resectable (BRPC) adenocarcinoma of the pancreas. Ann Surg Oncol 22: 1153–1159. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bruera E, Kuehn N, Miller MJ, Selmser P, Macmillan K (1991) The Edmonton Symptom Assessment System (ESAS): a simple method for the assessment of palliative care patients. J Palliat Care 7: 6–9. - PubMed
-
- Burris HA, 3rd, Moore MJ, Andersen J, Green MR, Rothenberg ML, Modiano MR, Cripps MC, Portenoy RK, Storniolo AM, Tarassoff P, Nelson R, Dorr FA, Stephens CD, von Hoff DD (1997) Improvements in survival and clinical benefit with gemcitabine as first-line therapy for patients with advanced pancreas cancer: a randomized trial. J Clin Oncol 15: 2403–2413. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

