Silencing the Transcriptional Repressor, ZCT1, Illustrates the Tight Regulation of Terpenoid Indole Alkaloid Biosynthesis in Catharanthus roseus Hairy Roots
- PMID: 27467510
- PMCID: PMC4965073
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0159712
Silencing the Transcriptional Repressor, ZCT1, Illustrates the Tight Regulation of Terpenoid Indole Alkaloid Biosynthesis in Catharanthus roseus Hairy Roots
Abstract
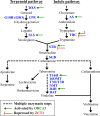
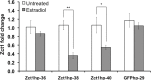
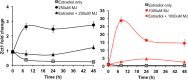
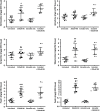
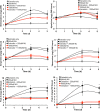
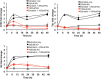
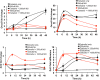
The Catharanthus roseus plant is the source of many valuable terpenoid indole alkaloids (TIAs), including the anticancer compounds vinblastine and vincristine. Transcription factors (TFs) are promising metabolic engineering targets due to their ability to regulate multiple biosynthetic pathway genes. To increase TIA biosynthesis, we elicited the TIA transcriptional activators (ORCAs and other unidentified TFs) with the plant hormone, methyl jasmonate (MJ), while simultaneously silencing the expression of the transcriptional repressor ZCT1. To silence ZCT1, we developed transgenic hairy root cultures of C. roseus that expressed an estrogen-inducible Zct1 hairpin for activating RNA interference. The presence of 17β-estradiol (5μM) effectively depleted Zct1 in hairy root cultures elicited with MJ dosages that either optimize or inhibit TIA production (250 or 1000μM). However, silencing Zct1 was not sufficient to increase TIA production or the expression of the TIA biosynthetic genes (G10h, Tdc, and Str), illustrating the tight regulation of TIA biosynthesis. The repression of the TIA biosynthetic genes at the inhibitory MJ dosage does not appear to be solely regulated by ZCT1. For instance, while Zct1 and Zct2 levels decreased through activating the Zct1 hairpin, Zct3 levels remained elevated. Since ZCT repressors have redundant yet distinct functions, silencing all three ZCTs may be necessary to relieve their repression of alkaloid biosynthesis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Repression of ZCT1, ZCT2 and ZCT3 affects expression of terpenoid indole alkaloid biosynthetic and regulatory genes.PeerJ. 2021 Jul 2;9:e11624. doi: 10.7717/peerj.11624. eCollection 2021. PeerJ. 2021. PMID: 34249496 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the ZCTs, a subgroup of Cys2-His2 zinc finger transcription factors regulating alkaloid biosynthesis in Catharanthus roseus.Plant Cell Rep. 2024 Aug 8;43(9):209. doi: 10.1007/s00299-024-03295-8. Plant Cell Rep. 2024. PMID: 39115578 Free PMC article.
-
The transcription factor CrWRKY1 positively regulates the terpenoid indole alkaloid biosynthesis in Catharanthus roseus.Plant Physiol. 2011 Dec;157(4):2081-93. doi: 10.1104/pp.111.181834. Epub 2011 Oct 11. Plant Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21988879 Free PMC article.
-
Terpenoid indole alkaloid biosynthesis in Catharanthus roseus: effects and prospects of environmental factors in metabolic engineering.Biotechnol Lett. 2021 Nov;43(11):2085-2103. doi: 10.1007/s10529-021-03179-x. Epub 2021 Sep 25. Biotechnol Lett. 2021. PMID: 34564757 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptional Regulation and Transport of Terpenoid Indole Alkaloid in Catharanthus roseus: Exploration of New Research Directions.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Dec 28;18(1):53. doi: 10.3390/ijms18010053. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 28036025 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Transcription Factors in Alkaloid Engineering.Biomolecules. 2021 Nov 18;11(11):1719. doi: 10.3390/biom11111719. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34827717 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ZCTs knockdown using antisense LNA GapmeR in specialized photomixotrophic cell suspensions of Catharanthus roseus: Rerouting the flux towards mono and dimeric indole alkaloids.Physiol Mol Biol Plants. 2021 Jul;27(7):1437-1453. doi: 10.1007/s12298-021-01017-y. Epub 2021 Jun 17. Physiol Mol Biol Plants. 2021. PMID: 34366588 Free PMC article.
-
UPLC/MS-based untargeted metabolomics reveals the changes of metabolites profile of Salvia miltiorrhiza bunge during Sweating processing.Sci Rep. 2020 Nov 11;10(1):19524. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-76650-w. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33177654 Free PMC article.
-
Repression of ZCT1, ZCT2 and ZCT3 affects expression of terpenoid indole alkaloid biosynthetic and regulatory genes.PeerJ. 2021 Jul 2;9:e11624. doi: 10.7717/peerj.11624. eCollection 2021. PeerJ. 2021. PMID: 34249496 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the ZCTs, a subgroup of Cys2-His2 zinc finger transcription factors regulating alkaloid biosynthesis in Catharanthus roseus.Plant Cell Rep. 2024 Aug 8;43(9):209. doi: 10.1007/s00299-024-03295-8. Plant Cell Rep. 2024. PMID: 39115578 Free PMC article.
References
-
- van der Heijden R, Jacobs DI, Snoeijer W, Hallard D, Verpoorte R (2004) The Catharanthus alkaloids: pharmacognosy and biotechnology. Curr Med Chem 11: 607–628. - PubMed
-
- Morgan JA, Shanks JV (2000) Determination of metabolic rate-limitations by precursor feeding in Catharanthus roseus hairy root cultures. J Biotechnol 79: 137–145. - PubMed
-
- Lee-Parsons CWT, Royce AJ (2006) Precursor limitations in methyl jasmonate-induced Catharanthus roseus cell cultures. Plant Cell Rep 25: 607–612. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

