Effects of Multidrug Resistant Tuberculosis Treatment on Patients' Health Related Quality of Life: Results from a Follow Up Study
- PMID: 27467560
- PMCID: PMC4965095
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0159560
Effects of Multidrug Resistant Tuberculosis Treatment on Patients' Health Related Quality of Life: Results from a Follow Up Study
Abstract
Background: At present, within the management of multidrug resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) much attention is being paid to the traditional microbiological and clinical indicators. Evaluation of the impact of MDR-TB treatment on patients' Health Related Quality of Life (HRQoL) has remained a neglected area.
Objective: To evaluate the impact of MDR-TB treatment on patients HRQoL, and determine the predictors of variability in HRQoL along the course of treatment.
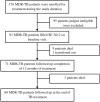
Methods: A prospective follow up study was conducted at the programmatic management unit for drug resistant TB of Lady Reading Hospital Peshawar. Culture confirmed eligible MDR-TB patients were asked to self complete SF-36v2 at the baseline visit, and subsequently after the completion of 12 months of treatment and at the end of treatment. A score of <47 norm-based scoring (NBS) points on component summary measures and health domain scales was considered indicative of function impairment. General linear model repeated measures ANOVA was used examine the change and predictors of change in physical component summary (PCS) and mental component summary (MCS) scores over the time.
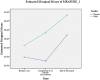
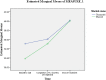
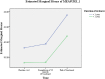
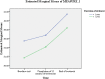
Results: A total of 68 out of enrolled 81 eligible MDR-TB patients completed SF-36v2 questionnaire at the three time points. Patients' mean PCS scores at the three time points were, 38.2±4.7, 38.6±4.4 and 42.2±5.2 respectively, and mean MCS were 33.7±7.0, 35.5±6.9 and 40.0±6.9 respectively. Length of sickness prior to the diagnosis of MDR-TB was predictive of difference in PCS scores (F = 4.988, Df = 1, 66), whereas patients' gender (F = 5.638, Df = 1, 66) and length of sickness prior to the diagnosis of MDR-TB (F = 4.400, Df = 1, 66) were predictive of difference in MCS scores.
Conclusion: Despite the positive impact of MDR-TB treatment on patients' HRQoL, the scores on component summary measures suggested compromised physical and mental health even at the end of treatment. A large multicenter study is suggested to confirm the present findings.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Health-related quality of life of patients with multidrug-resistant tuberculosis in Yemen: prospective study.Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2019 Aug 16;17(1):142. doi: 10.1186/s12955-019-1211-0. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2019. PMID: 31420045 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of tuberculosis treatment on health-related quality of life of pulmonary tuberculosis patients: a follow-up study.Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2014 Feb 14;12:19. doi: 10.1186/1477-7525-12-19. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2014. PMID: 24528499 Free PMC article.
-
The health-related quality of life of drug-resistant tuberculosis patients receiving treatment in Botswana.BMC Infect Dis. 2024 Nov 29;24(1):1367. doi: 10.1186/s12879-024-10258-7. BMC Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 39614181 Free PMC article.
-
Mental health disorders, social stressors, and health-related quality of life in patients with multidrug-resistant tuberculosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Infect. 2018 Nov;77(5):357-367. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2018.07.007. Epub 2018 Jul 20. J Infect. 2018. PMID: 30036607
-
Management of multi-drug resistant tuberculosis: practitioner's view point.Indian J Tuberc. 2007 Jan;54(1):3-11. Indian J Tuberc. 2007. PMID: 17455417 Review.
Cited by
-
Assessing the quality of life in patients with drug-resistant tuberculosis: a cross-sectional study.BMC Pulm Med. 2024 Jun 27;24(1):303. doi: 10.1186/s12890-024-03119-1. BMC Pulm Med. 2024. PMID: 38937809 Free PMC article.
-
Quality of life with tuberculosis.J Clin Tuberc Other Mycobact Dis. 2019 Sep 20;17:100121. doi: 10.1016/j.jctube.2019.100121. eCollection 2019 Dec. J Clin Tuberc Other Mycobact Dis. 2019. PMID: 31788563 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Dual Perspective of Psycho-Social Barriers and Challenges Experienced by Drug-Resistant TB Patients and Their Caregivers through the Course of Diagnosis and Treatment: Findings from a Qualitative Study in Bengaluru and Hyderabad Districts of South India.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Nov 10;11(11):1586. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11111586. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36358241 Free PMC article.
-
Provision of mental health care within primary care in Peru: A qualitative study exploring the perspectives of psychologists, primary health care providers, and patients.Wellcome Open Res. 2018 Feb 12;3:9. doi: 10.12688/wellcomeopenres.13746.2. eCollection 2018. Wellcome Open Res. 2018. PMID: 29623297 Free PMC article.
-
Quality of drug-resistant tuberculosis care: Gaps and solutions.J Clin Tuberc Other Mycobact Dis. 2019 Apr 24;16:100101. doi: 10.1016/j.jctube.2019.100101. eCollection 2019 Aug. J Clin Tuberc Other Mycobact Dis. 2019. PMID: 31720427 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Leidy NK, Revicki DA, Genesté B. Recommendations for evaluating the validity of quality of life claims for labeling and promotion. Value in Health. 1999; 2(2): 113–127. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

