Rituximab-based treatments followed by adoptive cellular immunotherapy for biopsy-proven EBV-associated post-transplant lymphoproliferative disease in recipients of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
- PMID: 27467959
- PMCID: PMC4910706
- DOI: 10.1080/2162402X.2016.1139274
Rituximab-based treatments followed by adoptive cellular immunotherapy for biopsy-proven EBV-associated post-transplant lymphoproliferative disease in recipients of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
Abstract
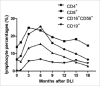
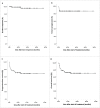
To improve prognosis of post-transplant lymphoproliferative disease (PTLD), a sequential therapeutic strategy that rituximab-based treatments followed by donor lymphocyte infusion (DLI) or autologous EBV-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes (EBV-CTL) for biopsy-proven EBV-associated PTLD in recipients of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation was designed. 84 patients with EBV-PTLD were enrolled in this prospective study. After two cycles of the rituximab-based treatments, 68 of 84 patients (81% [95% CI 71-88]) responded and 52 (62% [51-72]) had CRs. This increased to 73 of 77 patients (95% [87-98]) with completion of sequential cell infusions, and 70 of 77 (91% [82-96]) achieved CRs after DLI or autologous EBV-CTL infusion. 22 patients experienced acute GVHD (aGVHD) (grade I in 5 and grade II in 13, grade III in 4) and 13 chronic GVHD (limited cGVHD in 7 and extensive cGVHD in 6) in 62 patients undergoing a median of three doses of DLI. The incidences of GVHD were similar between DLI and EBV-CTL group (aGVHD 35% vs. 33%, p = 0.876; cGVHD 21% vs. 13%; p = 0.503). EBV-CTL activity after the rituximab-based treatments did not change, while increased after cell infusions and reached its maximum in the 3rd or 6th month after EBV-CTL or DLI treatment, respectively. The 5-y cumulative incidence of PTLD relapse was 4.5% ± 3.3%. The 5-y overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) after PTLD were 70.7% ± 5.2% and 68.9% ± 5.3%, respectively. Rituximab-based treatments combined with adoptive cellular immunotherapy might elevate CR rates and reduce relapse of PTLD after allo-HSCT.
Keywords: Adoptive cellular immunotherapy; EBV; EBV-CTL; PTLD; donor lymphocyte infusion; hematopoietic stem cell transplantation; relapse; rituximab.
Figures


References
-
- Styczynski J, Einsele H, Gil L, Ljungman P. Outcome of treatment of Epstein-Barr virus-related post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder in hematopoietic stem cell recipients: a comprehensive review of reported cases. Transpl Infect Dis 2009; 11:383-92; PMID:19558376; http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3062.2009.00411.x - DOI - PubMed
-
- Choquet S, Leblond V, Herbrecht R, Socie G, Stoppa AM, Vandenberqhe P, Fischer A, Morschhauser F, Salles G, Feremans W et al.. Efficacy and safety of rituximab in B-cell post-transplantation lymphoproliferative disorders: results of a prospective multicenter phase 2 study. Blood 2006; 107:3053-7; PMID:16254143; http://dx.doi.org/10.1182/blood-2005-01-0377 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Blaes AH, Peterson BA, Bartlett N, Dunn DL, Morrison VA. Rituximab therapy is effective for posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorders after solid organ transplantation: results of a phase II trial. Cancer 2005; 104:1661-7; PMID:16149091; http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/cncr.21391 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Choquet S, Oertel S, LeBlond V, Riess H, Varoqueaux N, Dörken B, Trappe R. Rituximab in the management of post-transplantation lymphoproliferative disorder after solid organ transplantation: proceed with caution. Ann Hematol 2007; 86:599-607; PMID:17522862; http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00277-007-0298-2 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Savoldo B, Rooney CM, Quiros-Tejeira RE, Caldwell Y, Wagner HJ, Lee T, Finegold MJ, Dotti G, Heslop HE, Goss JA. Cellular immunity to Epstein-Barr virus in liver transplant recipients treated with rituximab for post-transplant lymphoproliferative disease. Am J Transplant 2005; 5:566-72; PMID:15707412; http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-6143.2004.00693.x - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
