(19)F-MRI for monitoring human NK cells in vivo
- PMID: 27467963
- PMCID: PMC4910731
- DOI: 10.1080/2162402X.2016.1143996
(19)F-MRI for monitoring human NK cells in vivo
Abstract
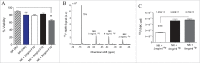
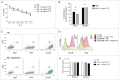
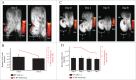
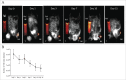
The availability of clinical-grade cytokines and artificial antigen-presenting cells has accelerated interest in using natural killer (NK) cells as adoptive cellular therapy (ACT) for cancer. One of the technological shortcomings of translating therapies from animal models to clinical application is the inability to effectively and non-invasively track these cells after infusion in patients. We have optimized the nonradioactive isotope fluorine-19 ((19)F) as a means to label and track NK cells in preclinical models using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Human NK cells were expanded with interleukin (IL)-2 and labeled in vitro with increasing concentrations of (19)F. Doses as low as 2 mg/mL (19)F were detected by MRI. NK cell viability was only decreased at 8 mg/mL (19)F. No effects on NK cell cytotoxicity against K562 leukemia cells were observed with 2, 4 or 8 mg/mL (19)F. Higher doses of (19)F, 4 mg/mL and 8 mg/mL, led to an improved (19)F signal by MRI with 3 × 10(11) (19)F atoms per NK cell. The 4 mg/mL (19)F labeling had no effect on NK cell function via secretion of granzyme B or interferon gamma (IFNγ), compared to NK cells exposed to vehicle alone. (19)F-labeled NK cells were detectable immediately by MRI after intratumoral injection in NSG mice and up to day 8. When (19)F-labeled NK cells were injected subcutaneously, we observed a loss of signal through time at the site of injection suggesting NK cell migration to distant organs. The (19)F perfluorocarbon is a safe and effective reagent for monitoring the persistence and trafficking of NK cell infusions in vivo, and may have potential for developing novel imaging techniques to monitor ACT for cancer.
Keywords: Fluorine 19 (19F); in vivo imaging and adoptive cell therapy (ACT); magnetic resonance imaging (MRI); natural killer cells (NKs).
Figures

Similar articles
-
Detection and viability of murine NK cells in vivo in a lymphoma model using fluorine-19 MRI.NMR Biomed. 2021 Dec;34(12):e4600. doi: 10.1002/nbm.4600. Epub 2021 Aug 18. NMR Biomed. 2021. PMID: 34409665 Free PMC article.
-
In-Vivo Detection and Tracking of T Cells in Various Organs in a Melanoma Tumor Model by 19F-Fluorine MRS/MRI.PLoS One. 2016 Oct 13;11(10):e0164557. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0164557. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27736925 Free PMC article.
-
Real-Time Tracking of Ex Vivo-Expanded Natural Killer Cells Toward Human Triple-Negative Breast Cancers.Front Immunol. 2018 May 2;9:825. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00825. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29770131 Free PMC article.
-
Aqueous colloidal nanoemulsion of perfluorocarbon polymers.2011 Feb 24 [updated 2011 Mar 31]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. 2011 Feb 24 [updated 2011 Mar 31]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. PMID: 21473038 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Fluorine-19 MRI for detection and quantification of immune cell therapy for cancer.J Immunother Cancer. 2018 Oct 11;6(1):105. doi: 10.1186/s40425-018-0416-9. J Immunother Cancer. 2018. PMID: 30305175 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Advances in NK cell therapy for brain tumors.NPJ Precis Oncol. 2023 Feb 15;7(1):17. doi: 10.1038/s41698-023-00356-1. NPJ Precis Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36792722 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic Value of Fluorine-19 MRI Oximetry Monitoring in cancer.Mol Imaging Biol. 2022 Apr;24(2):208-219. doi: 10.1007/s11307-021-01648-3. Epub 2021 Oct 27. Mol Imaging Biol. 2022. PMID: 34708396 Review.
-
Advanced Cancer Imaging Applied in the Comparative Setting.Front Oncol. 2020 Feb 7;10:84. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00084. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32117739 Free PMC article.
-
Preclinical and Clinical-Scale Magnetic Particle Imaging of Natural Killer Cells: in vitro and ex vivo Demonstration of Cellular Sensitivity, Resolution, and Quantification.Mol Imaging Biol. 2025 Feb;27(1):78-88. doi: 10.1007/s11307-024-01969-z. Epub 2024 Dec 9. Mol Imaging Biol. 2025. PMID: 39653984
-
Perfluorocarbons: A perspective of theranostic applications and challenges.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023 Aug 3;11:1115254. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1115254. eCollection 2023. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37600314 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arai S, Meagher R, Swearingen M, Myint H, Rich E, Martinson J, Klingemann H. Infusion of the allogeneic cell line NK-92 in patients with advanced renal cell cancer or melanoma: a phase I trial. Cytotherapy 2008; 10:625-32; PMID:18836917; http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/14653240802301872 - DOI - PubMed
-
- deMagalhaes-Silverman M, Donnenberg A, Lembersky B, Elder E, Lister J, Rybka W, Whiteside T, Ball E. Posttransplant adoptive immunotherapy with activated natural killer cells in patients with metastatic breast cancer. J Immunother 2000; 23:154-60; PMID:10687148; http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00002371-200001000-00018 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Geller MA, Cooley S, Judson PL, Ghebre R, Carson LF, Argenta PA, Jonson AL, Panoskaltsis-Mortari A, Curtsinger J, McKenna D et al.. A phase II study of allogeneic natural killer cell therapy to treat patients with recurrent ovarian and breast cancer. Cytotherapy 2011; 13:98-107; PMID:20849361; http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/14653249.2010.515582 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lister J, Rybka WB, Donnenberg AD, deMagalhaes-Silverman M, Pincus SM, Bloom EJ, Elder EM, Ball ED, Whiteside TL. Autologous peripheral blood stem cell transplantation and adoptive immunotherapy with activated natural killer cells in the immediate posttransplant period. Clin Cancer Res 1995; 1:607-14; PMID:9816022 - PubMed
-
- Miller JS, Soignier Y, Panoskaltsis-Mortari A, McNearney SA, Yun GH, Fautsch SK, McKenna D, Le C, Defor TE, Burns LJ et al.. Successful adoptive transfer and in vivo expansion of human haploidentical NK cells in patients with cancer. Blood. 2005 Apr 15; 105(8):3051-; PMID:15632206; http://dx.doi.org/10.1182/blood-2004-07-2974 - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
