Visualizing the hepatic vascular architecture using superb microvascular imaging in patients with hepatitis C virus: A novel technique
- PMID: 27468197
- PMCID: PMC4948259
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i26.6057
Visualizing the hepatic vascular architecture using superb microvascular imaging in patients with hepatitis C virus: A novel technique
Abstract
Aim: To identify the hepatic vascular architecture of patients with hepatitis C virus (HCV) using superb microvascular imaging (SMI) and investigate the use of SMI in the evaluation of liver fibrosis.
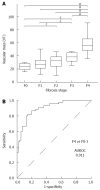
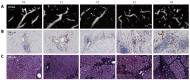
Methods: SMI was performed in 100 HCV patients. SMI images were classified into five types according to the vascular pattern, and these patterns were compared with the fibrosis stage. Moreover, the images were analyzed to examine vascularity by integrating the number of SMI signals in the region of interest ROI [number of vascular trees (VT)]. The number of VT, fibrosis stage, serum parameters of liver function, and CD34 expression were investigated.
Results: There was a significant difference between SMI distribution pattern and fibrosis stage (P < 0.001). The mean VT values in each of the fibrosis stages were as follows: 26.69 ± 7.08 in F0, 27.72 ± 9.32 in F1, 36.74 ± 9.23 in F2, 37.36 ± 5.32 in F3, and 58.14 ± 14.08 in F4. The VT showed excellent diagnostic ability for F4 [area under the receiver operator characteristic (AUROC): 0.911]. The VT was significantly correlated with the CD34 labeling index (r = 0.617, P < 0.0001).
Conclusion: SMI permitted the detailed delineation of the vascular architecture in chronic liver disease. SMI appears to be a reliable tool for noninvasively detecting significant fibrosis or cirrhosis in HCV patients.
Keywords: CD34; Chronic liver disease; Liver fibrosis; Number of vascular trees; Superb microvascular imaging; Ultrasound.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Radiology-pathology correlation in staging of liver fibrosis using superb microvascular imaging.Diagn Interv Radiol. 2019 Sep;25(5):331-337. doi: 10.5152/dir.2019.18231. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2019. PMID: 31287429 Free PMC article.
-
Non-invasive score system for fibrosis in chronic hepatitis: proposal for a model based on biochemical, FibroScan and ultrasound data.Liver Int. 2015 Aug;35(8):2027-35. doi: 10.1111/liv.12761. Epub 2015 Jan 21. Liver Int. 2015. PMID: 25495478
-
Accuracy of real-time shear wave elastography for assessing liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C: a pilot study.Hepatology. 2012 Dec;56(6):2125-33. doi: 10.1002/hep.25936. Epub 2012 Aug 31. Hepatology. 2012. PMID: 22767302
-
Performance of the aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index for the staging of hepatitis C-related fibrosis: an updated meta-analysis.Hepatology. 2011 Mar;53(3):726-36. doi: 10.1002/hep.24105. Epub 2011 Feb 11. Hepatology. 2011. PMID: 21319189 Review.
-
Clinical Applications of Superb Microvascular Imaging in the Superficial Tissues and Organs: A Systematic Review.Acad Radiol. 2021 May;28(5):694-703. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2020.03.032. Epub 2020 May 5. Acad Radiol. 2021. PMID: 32418782
Cited by
-
Liver fibrosis stage classification in stacked microvascular images based on deep learning.BMC Med Imaging. 2025 Jan 7;25(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s12880-024-01531-x. BMC Med Imaging. 2025. PMID: 39773130 Free PMC article.
-
Visualization of draining vein in focal nodular hyperplasia by superb microvascular imaging: report of two cases.J Med Ultrason (2001). 2017 Oct;44(4):323-328. doi: 10.1007/s10396-017-0775-8. Epub 2017 Feb 21. J Med Ultrason (2001). 2017. PMID: 28224304
-
Comparison of superb microvascular imaging and shear wave elastography for assessing liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B.Ultrasonography. 2022 Apr;41(2):394-402. doi: 10.14366/usg.21136. Epub 2021 Nov 25. Ultrasonography. 2022. PMID: 35026886 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of the utility of two-dimensional shear wave elastography and superb microvascular imaging in postoperative patients with biliary atresia.Pediatr Surg Int. 2024 Aug 8;40(1):219. doi: 10.1007/s00383-024-05804-y. Pediatr Surg Int. 2024. PMID: 39115726
-
The utility of superb microvascular imaging for monitoring low-velocity venous flow following pancreas transplantation: report of a case.J Med Ultrason (2001). 2018 Jan;45(1):171-174. doi: 10.1007/s10396-017-0795-4. Epub 2017 Jun 8. J Med Ultrason (2001). 2018. PMID: 28597330
References
-
- Krahn M, Wong JB, Heathcote J, Scully L, Seeff L. Estimating the prognosis of hepatitis C patients infected by transfusion in Canada between 1986 and 1990. Med Decis Making. 2004;24:20–29. - PubMed
-
- Serfaty L, Aumaître H, Chazouillères O, Bonnand AM, Rosmorduc O, Poupon RE, Poupon R. Determinants of outcome of compensated hepatitis C virus-related cirrhosis. Hepatology. 1998;27:1435–1440. - PubMed
-
- Wanless IR, Wong F, Blendis LM, Greig P, Heathcote EJ, Levy G. Hepatic and portal vein thrombosis in cirrhosis: possible role in development of parenchymal extinction and portal hypertension. Hepatology. 1995;21:1238–1247. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

