Extensive deep vein thrombosis treatment using fondaparinux and edoxaban: a case report
- PMID: 27468257
- PMCID: PMC4962499
- DOI: 10.1186/s12959-016-0089-x
Extensive deep vein thrombosis treatment using fondaparinux and edoxaban: a case report
Abstract
Background: Factor Xa inhibitor is a key drug in the coagulation cascade. Parenteral anticoagulation using low molecular weight heparin or fondaparinux is the recommended form of treatment for most patients presenting with venous thrombosis. Following the acute phase, edoxaban is recommended. We present a case of extensive deep vein thrombosis treated using fondaparinux and edoxaban.
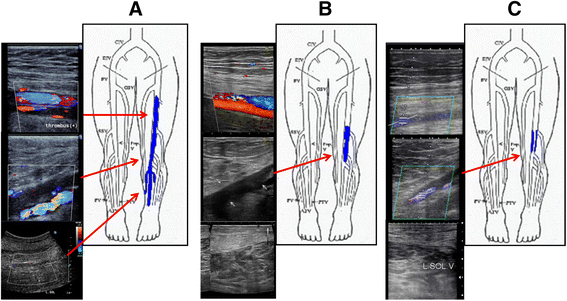
Case presentation: A 63-year-old man with redness, pain, and swelling of the left leg lasting for more than 1 month was referred to our hospital. Ultrasonography revealed a thrombus in the left femoral vein. Computed tomographic angiography revealed clots in the distal right pulmonary artery. Thus, the anticoagulant treatment was initiated with subcutaneous injections of fondaparinux (7.5 mg) for 5 consecutive days, followed by once daily oral administration of edoxaban (60 mg). After 3 months of treatment, a regression of thrombotic clots was shown. Three months later, the remaining clots disappeared, leaving only mural thrombi; no bleeding complications were observed during the treatment period.
Conclusion: The anticoagulant treatment with subcutaneous fondaparinux and subsequently with oral edoxaban was effective for treating extensive deep vein thrombosis.
Keywords: Deep vein thrombosis; Edoxaban; Factor Xa inhibitor; Fondaparinux; Venous thromoboembolism.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Short-Term Subcutaneous Fondaparinux and Oral Edoxaban for Acute Venous Thromboembolism.Circ J. 2017 May 25;81(6):855-861. doi: 10.1253/circj.CJ-16-1012. Epub 2017 Feb 25. Circ J. 2017. PMID: 28239036 Clinical Trial.
-
Treatment of venous thrombosis with an oral direct factor Xa inhibitor edoxaban by single and multiple administrations in rats.Eur J Pharmacol. 2014 Nov 5;742:15-21. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.08.020. Epub 2014 Aug 30. Eur J Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25179572
-
Magnetic resonance venography to assess thrombus resolution with edoxaban monotherapy versus parenteral anticoagulation/warfarin for symptomatic deep vein thrombosis: A multicenter feasibility study.Vasc Med. 2016 Aug;21(4):361-8. doi: 10.1177/1358863X16645853. Epub 2016 May 10. Vasc Med. 2016. PMID: 27165711 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Managing pulmonary embolism from presentation to extended treatment.Thromb Res. 2014 Feb;133(2):139-48. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2013.09.040. Epub 2013 Oct 14. Thromb Res. 2014. PMID: 24182642 Review.
-
[Therapy and prevention of deep venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism in gynecology and obstetrics].Acta Med Croatica. 2003;57(2):123-30. Acta Med Croatica. 2003. PMID: 12879692 Review. Croatian.
Cited by
-
Treatment of pulmonary thromboembolism with edoxaban in a cancer patient with borderline fulfillment of the dose reduction criteria.SAGE Open Med Case Rep. 2019 Sep 23;7:2050313X19878047. doi: 10.1177/2050313X19878047. eCollection 2019. SAGE Open Med Case Rep. 2019. PMID: 31579511 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Raskob G, Cohen AT, Eriksson BI, Puskas D, Shi M, Bocanegra T, et al. Oral direct factor Xa inhibition with edoxaban for thromboprophylaxis after elective total hip replacement: a randomised double-blind dose–response study. Thromb Haemost. 2010;104:642–649. doi: 10.1160/TH10-02-0142. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Weitz JI, Connolly SJ, Patel I, Salazar D, Rohatagi S, Mendell J, et al. Randomised, parallel-group, multicentre, multinational phase 2 study comparing edoxaban, an oral factor Xa inhibitor, with warfarin for stroke prevention in patients with atrial fibrillation. Thromb Haemost. 2010;104:633–641. doi: 10.1160/TH10-01-0066. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

