Establishing normative foot posture index values for the paediatric population: a cross-sectional study
- PMID: 27468312
- PMCID: PMC4962378
- DOI: 10.1186/s13047-016-0156-3
Establishing normative foot posture index values for the paediatric population: a cross-sectional study
Abstract
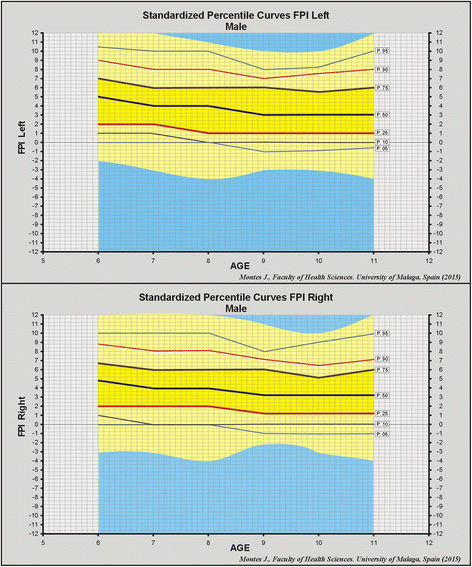
Background: The Foot Posture Index (FPI) is an observational tool designed to measure the position of the foot. Its reliability is well established, and it provides normative reference values for the general population. However, this is not so for the paediatric population. The aim of this study is to determine FPI reference values in childhood, taking into account age and gender.
Methods: This cross-sectional study included 1,762 school children (863 boys and 899 girls) aged 6-11 years, from Málaga, Granada and Plasencia (Spain). In every case, FPI measurements were obtained for both feet by two experienced podiatrists. A descriptive analysis was then conducted and the percentiles of the variables determined, with a significance level of P < 0.05.
Results: The consolidated FPI results for the sample population produced mean values of 3.74 (SD 2.93) points for the right foot and 3.83 (SD 2.92) for the left. The 50th percentile was 4 points for both genders and for both feet, except for the right foot among the girls, which was slightly lower, at 3 points. The 85th percentile, which is considered to represent the boundary between the normal and the pronated foot among children, was 6 points, uniformly among the subjects.
Conclusions: As a normative FPI value for the paediatric population, we recommend the 50th percentile, i.e. 4 points, for children, of both genders, aged 6 years. This value progressively falls with age, to 3 FPI points for children aged 11 years. The 85th percentile for the pronated foot and the 4th percentile for the supinated foot can be considered the pathological boundary.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The influence of gender and body mass index on the FPI-6 evaluated foot posture of 10- to 14-year-old school children in São Paulo, Brazil: a cross-sectional study.J Foot Ankle Res. 2017 Jun 27;10:1. doi: 10.1186/s13047-016-0183-0. eCollection 2017. J Foot Ankle Res. 2017. PMID: 28670344 Free PMC article.
-
Normative values for the foot posture index between right and left foot: a descriptive study.Gait Posture. 2013 Sep;38(4):843-6. doi: 10.1016/j.gaitpost.2013.04.006. Epub 2013 May 9. Gait Posture. 2013. PMID: 23665064
-
Influence of Age, Sex, and Anthropometric Determinants on the Foot Posture Index in a Pediatric Population.J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 2017 Mar;107(2):124-129. doi: 10.7547/14-097. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 2017. PMID: 28394675
-
Biomechanics of the Ageing Foot and Ankle: A Mini-Review.Gerontology. 2015;61(4):381-8. doi: 10.1159/000368357. Epub 2014 Nov 11. Gerontology. 2015. PMID: 25402236 Review.
-
Two-dimensional digital photography for child body posture evaluation: standardized technique, reliable parameters and normative data for age 7-10 years.Scoliosis Spinal Disord. 2017 Dec 19;12:38. doi: 10.1186/s13013-017-0146-7. eCollection 2017. Scoliosis Spinal Disord. 2017. PMID: 29276784 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Novel Deep Transfer Learning-Based Approach for Automated Pes Planus Diagnosis Using X-ray Image.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 May 8;13(9):1662. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13091662. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37175053 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Dental Malocclusion on Body Posture and Foot Posture in Children: A Cross-Sectional Study.Healthcare (Basel). 2020 Nov 14;8(4):485. doi: 10.3390/healthcare8040485. Healthcare (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33202576 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Shoe Characteristics on the Development of Valgus Foot in Children.J Clin Med. 2019 Jan 12;8(1):85. doi: 10.3390/jcm8010085. J Clin Med. 2019. PMID: 30642069 Free PMC article.
-
The influence of gender and body mass index on the FPI-6 evaluated foot posture of 10- to 14-year-old school children in São Paulo, Brazil: a cross-sectional study.J Foot Ankle Res. 2017 Jun 27;10:1. doi: 10.1186/s13047-016-0183-0. eCollection 2017. J Foot Ankle Res. 2017. PMID: 28670344 Free PMC article.
-
International normative data for paediatric foot posture assessment: a cross-sectional investigation.BMJ Open. 2019 Apr 14;9(4):e023341. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-023341. BMJ Open. 2019. PMID: 30987983 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bordelon RL. Hypermobile flatfoot in children. Comprehension, evaluation, and treatment. Clin Orthop. 1983;181:7–14. - PubMed
-
- McCarthy DJ. The developmental anatomy of pes valgo planus. Clin Podiatr Med Surg. 1989;6(3):491–509. - PubMed
-
- Onodera AN, Sacco ICN, Morioka EH, Souza PS, de Sá MR, Amadio AC. What is the best method for child longitudinal plantar arch assessment and when does arch maturation occur? Foot Edinb Scotl. 2008;18(3):142–9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials