Impact of metabolic syndrome on lipid target achievements in the Arabian Gulf: findings from the CEPHEUS study
- PMID: 27468314
- PMCID: PMC4962507
- DOI: 10.1186/s13098-016-0160-6
Impact of metabolic syndrome on lipid target achievements in the Arabian Gulf: findings from the CEPHEUS study
Abstract
Background: The aim of this study was to determine the impact of metabolic syndrome (MetS) on lipid target achievements in the Arabian Gulf.
Methods: The centralized pan-middle east survey on the undertreatment of hypercholesterolemia (CEPHEUS) included 4171 high and very high atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) risk patients from six Arabian Gulf countries. Analyses were performed using univariate statistics.
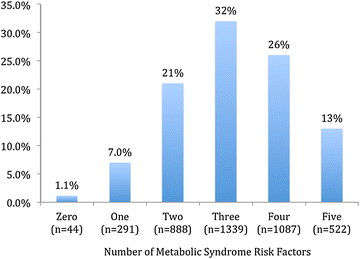
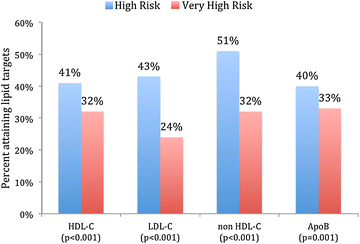
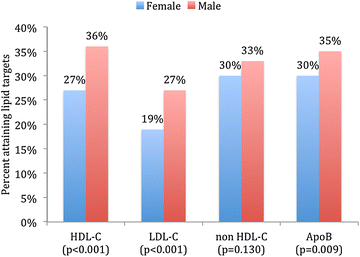
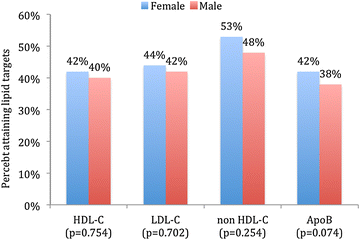
Results: The overall mean age was 57 ± 11 years, 41 % were females and 71 % had MetS. MetS patients were less likely to attain their HDL-C (34 vs. 79 %; P < 0.001), LDL-C (27 vs. 37 %; P < 0.001), non HDL-C (35 vs. 55 %; P < 0.001) and Apo B (35 vs. 54 %; P < 0.001) compared to those without MetS. Within the MetS cohort, those with very high ASCVD risk were less likely to attain their lipid targets compared to those with high ASCVD risk [HDL-C (32 vs. 41 %; P < 0.001), LDL-C (24 vs. 43 %; P < 0.001), non HDL-C (32 vs. 51 %; P < 0.001) and Apo B (33 vs. 40 %; P = 0.001)]. In those with MetS and very high ASCVD risk status, females were less likely to attain their HDL-C (27 vs. 36 %; P < 0.001), LDL-C (19 vs. 27 %; P < 0.001) and Apo B (30 vs. 35 %; P = 0.009) compared to males.
Conclusions: MetS was associated with low lipid therapeutic targets. Women and those with very high ASCVD risk were also less likely to attain their lipid targets in the Arabian Gulf.
Keywords: Arabian Gulf; Blood pressure; Cardiovascular diseases; HDL cholesterol; LDL cholesterol; Metabolic syndrome; Obesity; Triglycerides.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Gender Disparity in Lipid Target Achievements in High and Very High Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease Risk Patients in the Arabian Gulf.Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2017;15(1):51-58. doi: 10.2174/1570161114666161003095139. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 27697065
-
Therapeutic lipid target achievements among high and highest risk patients: results from the CEPHEUS study in the Arabian Gulf.Curr Med Res Opin. 2014 Dec;30(12):2429-35. doi: 10.1185/03007995.2014.965774. Epub 2014 Sep 29. Curr Med Res Opin. 2014. PMID: 25222765
-
Non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol target achievement in patients on lipid-lowering drugs and stratified by triglyceride levels in the Arabian Gulf.J Clin Lipidol. 2016 Mar-Apr;10(2):368-77. doi: 10.1016/j.jacl.2015.12.021. Epub 2015 Dec 23. J Clin Lipidol. 2016. PMID: 27055968
-
Lowering Targeted Atherogenic Lipoprotein Cholesterol Goals for Patients at "Extreme" ASCVD Risk.Curr Diab Rep. 2019 Nov 21;19(12):146. doi: 10.1007/s11892-019-1246-y. Curr Diab Rep. 2019. PMID: 31754844 Review.
-
Is non-high-density lipoprotein associated with metabolic syndrome? A systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Sep 13;13:957136. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.957136. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36176470 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

