Sweet-P inhibition of glucocorticoid receptor β as a potential cancer therapy
- PMID: 27468424
- PMCID: PMC4959805
Sweet-P inhibition of glucocorticoid receptor β as a potential cancer therapy
Abstract
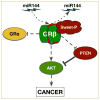
The need for the development of new cancer therapies and push for the design of new targeting techniques is on the rise, and would be useful for cancers that are resistant to current drug treatments. The understanding of the genome has significantly advanced cancer therapy, as well as prevention and earlier detection. This research highlight discusses a potential new type of cancer-targeting molecule, Sweet-P, which is the first of its kind. Sweet-P specifically targets the microRNA-144 binding site in the 3' untranslated region (3' UTR) of the human glucocorticoid receptor β (GRβ), which has been demonstrated to increase expression. GRβ has been shown to be highly expressed in cells from solid tumors of uroepithelial carcinomas, gliomas, osteosarcomas, and hepatocellular carcinomas, as well as in liquid tumor cells from leukemia patients. In non-cancerous diseases, GRβ has been shown to be highly expressed in glucocorticoid-resistant asthma. These maladies brought the need for the development of the Sweet-P anti-GRβ molecule. Sweet-P was shown to repress the migration of bladder cancer cells, and may serve as a new therapeutic for GRβ-related diseases.
Keywords: GR; GR alpha; GR beta; Glucocorticoid receptor; Sweet-P; asthma; bladder cancer; cancer; glucocorticoids; growth; miRNA; microRNA; migration.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no conflict of interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Society AC. Cancer Facts & Figures 2015. Atlanta, Ga: American Cancer Society; 2015.
-
- Duma D, Jewell CM, Cidlowski JA. Multiple glucocorticoid receptor isoforms and mechanisms of post-translational modification. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2006:11–21. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources