The Central domain of RyR1 is the transducer for long-range allosteric gating of channel opening
- PMID: 27468892
- PMCID: PMC5034110
- DOI: 10.1038/cr.2016.89
The Central domain of RyR1 is the transducer for long-range allosteric gating of channel opening
Abstract
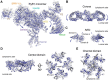
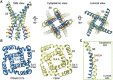
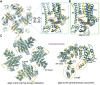
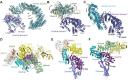
The ryanodine receptors (RyRs) are intracellular calcium channels responsible for rapid release of Ca(2+) from the sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum (SR/ER) to the cytoplasm, which is essential for the excitation-contraction (E-C) coupling of cardiac and skeletal muscles. The near-atomic resolution structure of closed RyR1 revealed the molecular details of this colossal channel, while the long-range allosteric gating mechanism awaits elucidation. Here, we report the cryo-EM structures of rabbit RyR1 in three closed conformations at about 4 Å resolution and an open state at 5.7 Å. Comparison of the closed RyR1 structures shows a breathing motion of the cytoplasmic platform, while the channel domain and its contiguous Central domain remain nearly unchanged. Comparison of the open and closed structures shows a dilation of the S6 tetrahelical bundle at the cytoplasmic gate that leads to channel opening. During the pore opening, the cytoplasmic "O-ring" motif of the channel domain and the U-motif of the Central domain exhibit coupled motion, while the Central domain undergoes domain-wise displacement. These structural analyses provide important insight into the E-C coupling in skeletal muscles and identify the Central domain as the transducer that couples the conformational changes of the cytoplasmic platform to the gating of the central pore.
Figures



References
-
- Pessah IN, Waterhouse AL, Casida JE. The calcium-ryanodine receptor complex of skeletal and cardiac muscle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1985; 128:449–456. - PubMed
-
- Inui M, Saito A, Fleischer S. Purification of the ryanodine receptor and identity with feet structures of junctional terminal cisternae of sarcoplasmic reticulum from fast skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem 1987; 262:1740–1747. - PubMed
-
- Lai FA, Erickson HP, Rousseau E, Liu QY, Meissner G. Purification and reconstitution of the calcium release channel from skeletal muscle. Nature 1988; 331:315–319. - PubMed
-
- Takeshima H, Nishimura S, Matsumoto T, et al. Primary structure and expression from complementary DNA of skeletal muscle ryanodine receptor. Nature 1989; 339:439–445. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

